Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) provides cellular energy, participates in overall energy balance, and maintains intracellular homeostasis. ATP can act as an extracellular signaling molecule through interactions with specific purinergic receptors to mediate a variety of processes including neurotransmission, inflammation, apoptosis, and bone remodeling.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $34 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $78 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $113 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) provides cellular energy, participates in overall energy balance, and maintains intracellular homeostasis. ATP can act as an extracellular signaling molecule through interactions with specific purinergic receptors to mediate a variety of processes including neurotransmission, inflammation, apoptosis, and bone remodeling. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Synovial fibroblast HSF were rapidly treated (wash-in and wash-out ~2 s) with ATP (10 μM) three times, and [Ca2+] changes were detected using Fluo-4 fluorescence. RESULTS: During the first application of ATP, Fluo-4 fluorescence increased rapidly after a delay of a few seconds and decreased slightly before the end of ATP application. After removal of ATP, the fluorescence signal returned to resting levels, but fluorescence decreased much more slowly than it had begun after the initial ATP application. The two subsequent ATP applications produced a response of less amplitude than the first, and the delay until the onset of the response appeared to lengthen with successive applications. [1] METHODS: Mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages BMDM were stimulated with LPS, HKEC, or HKSA, followed by treatment with ATP (2 mM) for 0.5-24 h. Levels of IL-1β, KC, and MIP-2 were determined using ELISA. RESULTS: ATP treatment strongly induced the secretion of IL-1β, KC and MIP-2. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To test the antibacterial activity in vivo, ATP (50 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally into Kunming mice, and E. coli 25922 or S. aureus 25923 was injected 1-24 h later. RESULTS: The administration of ATP 4 h or 24 h before the attack did significantly increase the survival rate of infected mice, regardless of the bacterial type. [2] METHODS: To assay in vivo antibacterial activity, ATP (40 mg/kg), clarithromycin (12 mg/kg), and rifampin (8 mg/kg) were injected subcutaneously into MAC-infected BALB/c mice five times per week for eight weeks. RESULTS: Co-administration of ATP with clarithromycin and rifampin accelerated bacterial clearance in MAC-infected mice without resulting in changes in histopathologic features or mRNA expression of pro- or anti-inflammatory cytokines in mice not given ATP. [3] |
| Synonyms | Triphosphoric acid adenosine ester, Triphosphaden, Atipi, Ara-ATP, Adenosine triphosphate |
| Molecular Weight | 507.18 |
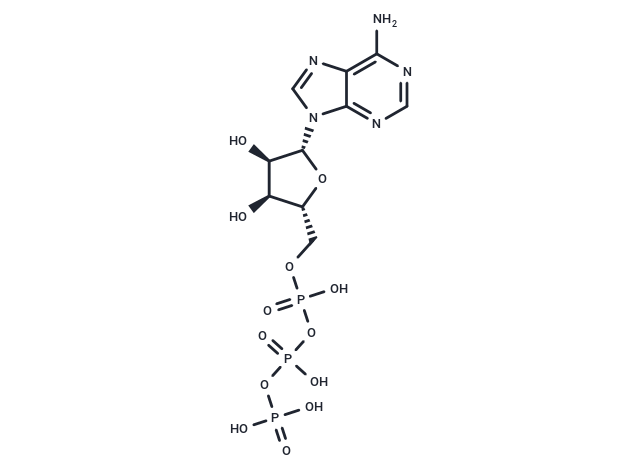
| Formula | C10H16N5O13P3 |
| Cas No. | 56-65-5 |
| Smiles | O[C@H]1[C@H](N2C=3C(N=C2)=C(N)N=CN3)O[C@H](COP(OP(OP(=O)(O)O)(=O)O)(=O)O)[C@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.0 g/cm3 at 20℃ |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | keep away from moisture,keep away from direct sunlight,store at low temperature,store under nitrogen | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 1.67 mg/mL (3.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 118.8 mg/mL (234.24 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.