Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


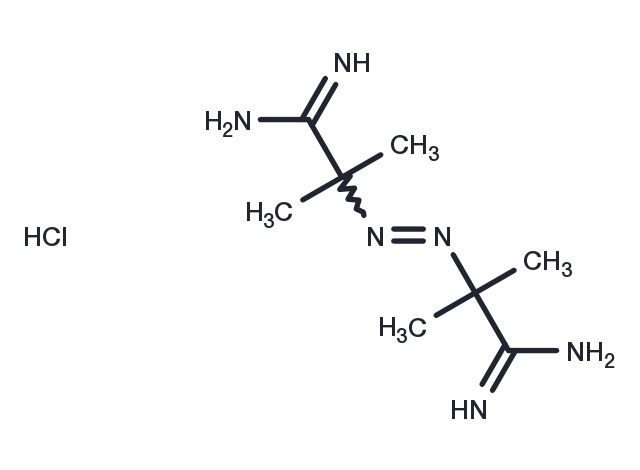
AAPH is a water-soluble azo compound which is used extensively as a free radical generator, often in the study of lipid peroxidation and the characterization of antioxidants.[1],[2],[3],[4] Decomposition of AAPH produces molecular nitrogen and 2 carbon radicals. The carbon radicals may combine to produce stable products or react with molecular oxygen to give peroxyl radicals. The half-life of AAPH is about 175 hours (37°C at neutral pH), making the rate of free radical generation essentially constant during the first several hours in solution.[5] While AAPH may be used effectively for lipid peroxidation in aqueous dispersions of fatty acids, other radical generators may be better suited for peroxidation studies in lipid micelles or membranes.[6],[7]
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 g | 35 days | $ 158.00 | |
| 10 g | 35 days | $ 265.00 |
| Description | AAPH is a water-soluble azo compound which is used extensively as a free radical generator, often in the study of lipid peroxidation and the characterization of antioxidants.[1],[2],[3],[4] Decomposition of AAPH produces molecular nitrogen and 2 carbon radicals. The carbon radicals may combine to produce stable products or react with molecular oxygen to give peroxyl radicals. The half-life of AAPH is about 175 hours (37°C at neutral pH), making the rate of free radical generation essentially constant during the first several hours in solution.[5] While AAPH may be used effectively for lipid peroxidation in aqueous dispersions of fatty acids, other radical generators may be better suited for peroxidation studies in lipid micelles or membranes.[6],[7] |
| Molecular Weight | 234.73 |
| Formula | C8H19ClN6 |
| CAS No. | 2997-92-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
PBS (pH 7.2): 10 mg/mL
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
AAPH 2997-92-4 inhibitor inhibit
