 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Rose Bengal sodium is a potent inhibitor of VGlut and vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) (Ki of 19 and 64 nM for VGlut andVMAT, respectively)
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $39 | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 100 mg | $64 | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 200 mg | $93 | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 500 mg | $153 | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Rose Bengal sodium is a potent inhibitor of VGlut and vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) (Ki of 19 and 64 nM for VGlut andVMAT, respectively) |
| In vitro | Instructions: a. Solution preparation: 1. Dissolve Rose Bengal sodium in DMSO to prepare a 10mM stock solution. Keep it away from light. Please divide the stock solution and store it at -20℃ or -80℃ to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. 2. Dilute the mother solution into a certain gradient of working solution for use. b. Operation steps: 1. Grow the bacteria to a concentration of 10^8 CFU/mL, and then dilute it tenfold with sterile saline to a concentration of 10^3-10^7 CFU/mL. 2. Transfer 3 mL of bacterial suspension to a flat-bottomed 20 mL vial with a diameter of 2.5 cm. Before the experiment, take a sample from each vial to determine the initial bacterial concentration. 3. Add different concentrations of Rose Bengal sodium to all vials except the control group. After adding Rose Bengal sodium, all subsequent operations are performed under dark conditions. 4. Place the vials of bacterial suspension with or without Rose Bengal sodium at the bottom of the ultrasound tank in a VU03H plastic holder and treat with ultrasound at a frequency of 38 kHz and an electric field strength of 4.1 W/cm^3 for 1 to 10 minutes. 5. After treatment, 100 μL of the sample was diluted tenfold and plated on a BHA plate. The plate was incubated overnight at 37°C and the bacterial cell concentration was determined using the viable count method. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Cell Research | Bacteria were grown to a concentration of 10^8 CFU/mL and then diluted with sterile saline by serial decimal dilutions to concentrations of 10^3–10^7 CFU/mL.?Three milliliters of bacterial suspensions was transferred into flat-bottom 2.5 cm diameter 20 mL vials.?Before the experiment, samples were taken from each vial to determine the initial bacterial concentration.?Free Rose Bengal at various concentrations or Rose Bengal immobilized onto silicone was added to all vials, except for the controls.?After adding Rose Bengal, all subsequent procedures were performed under dark conditions.?Vials with bacterial suspensions with or without Rose Bengal were held tight to the bottom of an ultrasonic bath in a plastic holder VU03H ?and treated by ultrasound at a frequency of 38 kHz and a field strength of 4.1 W/cm^3 for 1 to 10 min. After the treatment, 100 μL samples were diluted by several decimal dilutions and were spread over BHA plates with a Drigalsky spreader.?The plates were incubated at 37 °C overnight and the bacterial cell concentration was determined taking dilutions into account using the viable count method, where CFU were counted by means of a colony counter Scan 500.?In control experiments, bacterial cultures were tested in the absence of Rose Bengal without sonication, in the absence of Rose Bengal under sonication and in the presence of Rose Bengal without sonication[1]. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Molecular Weight | 1017.64 |
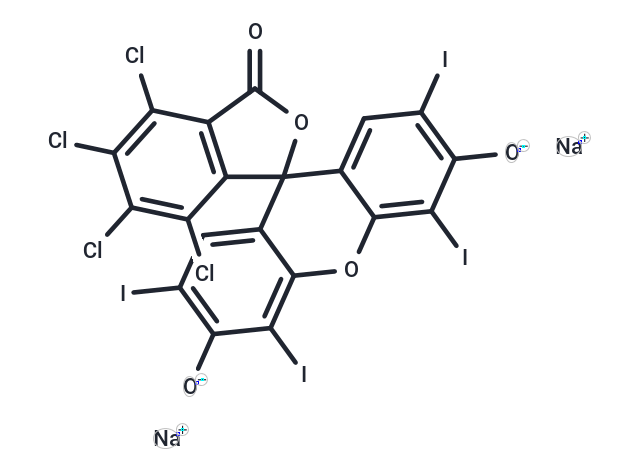
| Formula | C20H2Cl4I4Na2O5 |
| Cas No. | 632-69-9 |
| Smiles | [Na+].[Na+].[O-]c1c(I)cc2c(Oc3c(I)c([O-])c(I)cc3C22OC(=O)c3c2c(Cl)c(Cl)c(Cl)c3Cl)c1I |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 22.5 mg/mL (22.11 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.