 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Elgodipine significantly reduced the incidence and severity of exercise-induced angina pectoris systemically and was able to inhibit vascular smooth muscle proliferation through a mechanism independent of the expression of the transcription factors c-fos and c-jun. The Elgodipine-induced inhibition was voltage-dependent. Elgodipine is a potential compound for the treatment of angina pectoris.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $54 | - | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $133 | - | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $197 | - | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $323 | - | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $475 | - | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $678 | - | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $903 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Elgodipine significantly reduced the incidence and severity of exercise-induced angina pectoris systemically and was able to inhibit vascular smooth muscle proliferation through a mechanism independent of the expression of the transcription factors c-fos and c-jun. The Elgodipine-induced inhibition was voltage-dependent. Elgodipine is a potential compound for the treatment of angina pectoris. |
| Targets&IC50 | Ca2+ channel:0.33 µM |
| In vivo | Elgodipine (64 micrograms/kg; i.v.; 22 patients) significantly decreased systemic vascular resistance as well as systolic and diastolic blood pressure, while increasing cardiac output and stroke volume. Heart rate was not affected by elgodipine, either at rest or during exercise.[1] |
| Molecular Weight | 524.58 |
| Formula | C29H33FN2O6 |
| Cas No. | 119413-55-7 |
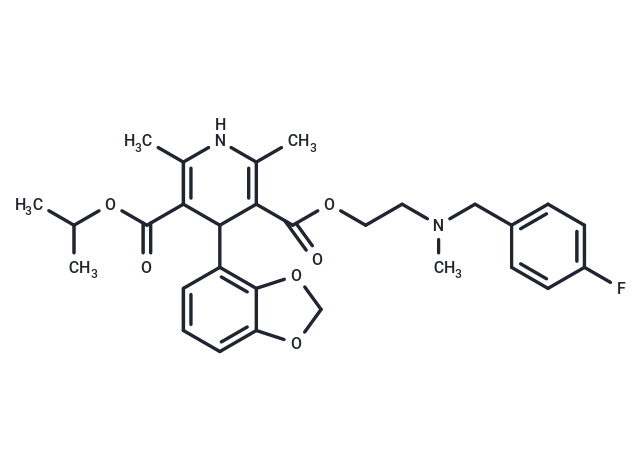
| Smiles | C(OCCN(CC1=CC=C(F)C=C1)C)(=O)C=2C(C(C(OC(C)C)=O)=C(C)NC2C)C3=C4C(=CC=C3)OCO4 |
| Storage | Pure form: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (104.85 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.