 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

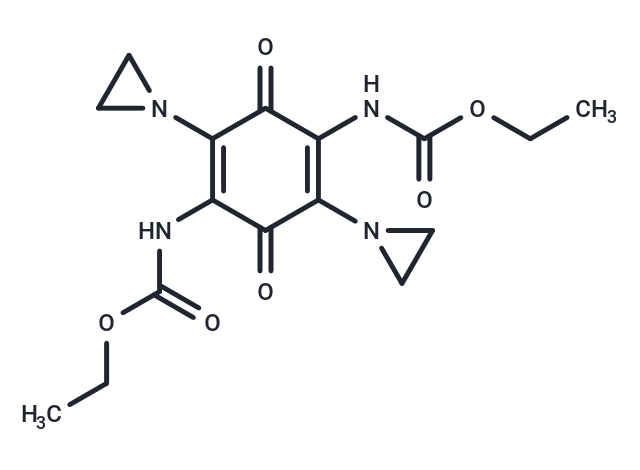
Diaziquone (NSC-182986) is a water-soluble synthetic azacyclic benzoquinone that enhances penetration of the blood-brain barrier, has antitumor activity, and is used in the treatment of extreme renal failure.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $147 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $372 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $596 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $976 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Diaziquone (NSC-182986) is a water-soluble synthetic azacyclic benzoquinone that enhances penetration of the blood-brain barrier, has antitumor activity, and is used in the treatment of extreme renal failure. |
| In vitro | Diaziquone (5000 ng/mL) is associated with prolonged aplasia and rare instances of bone marrow necrosis, but only mild extramedullary toxicity. One- and three-hour treatments produced little cytotoxicity for hematopoietic versus marrow stromal cells. After six-hour treatments with this dose, marrow was depleted of CFU-Mix, BFU-E, and CFU-GM, but produced CFU-GM in LTMCs, indicating an ongoing input of CFU-GM from a surviving pre-CFU-Mix population. Diaziquone (150 ng/mL; 3 to 7 days) elimination of the latter may be inferred from the absence of CFU-GM in the LTMCs exposed.[4] |
| In vivo | Diaziquone (0.1 mg/day; injection; 4 days) applied topically in Vanicream, Plastibase, or DMSO inhibited tumor growth at day 20 by 66, 86, and 43%, respectively, and cured animals of the skin tumor at a dose of 0.5 mg/day. Diaziquone administered i.p. at 0.5 mg/day for 4 days was lethal to rats, and at 0.1 mg/day it produced 93% inhibition of tumor growth at day 20. Diaziquone was applied topically at 0.1 mg/day for 4 days in Plastibase-cured rats of advanced tumors when treatment was begun 12 days after injection of tumor cells. The area under the plasma radioactivity time curve over 5 h for a single 0.64-mg dose of topically applied [ring-14C]diaziquone in DMSO was 0.01% that of the same dose of [ring-14C]diaziquone administered i.p. in non-tumored rats. The decrease in WBC count following topical application of diaziquone at a dose of 0.1 mg/day for 4 days, compared to the same dose of diaziquone administered i.p., was 62% in Vanicream, 81% in Plastibase and 33% in DMSO. Topical diaziquone was non-toxic to normal skin in the rat and in the domestic pig. It is concluded that topical application of diaziquone offers a therapeutic advantage over systemic treatment for metastatic cancer of the skin.[2] |
| Synonyms | NSC 182986 |
| Molecular Weight | 364.35 |
| Formula | C16H20N4O6 |
| Cas No. | 57998-68-2 |
| Smiles | N(C(OCC)=O)C1=C(C(=O)C(NC(OCC)=O)=C(C1=O)N2CC2)N3CC3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (123.51 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.