Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Vadimezan (DMXAA) is a vascular disrupting agent, a murine STING agonist, and an inducer of cytokines such as type I IFN. Vadimezan has antitumor activity and induces a rapid cessation of blood flow in tumors without affecting blood flow in normal tissues.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $35 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $56 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $89 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $185 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $297 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $446 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $645 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $86 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Vadimezan (DMXAA) is a vascular disrupting agent, a murine STING agonist, and an inducer of cytokines such as type I IFN. Vadimezan has antitumor activity and induces a rapid cessation of blood flow in tumors without affecting blood flow in normal tissues. |
| Targets&IC50 | A549 cells:> 100 μM, Bel-7402 cells:> 100 μM, BGC-823 cells:> 100 μM, DT diaphorase:20 μM (Ki), LY1 cells:177 μM, LY3 cells:165 μM, HeLa cells:> 100 μM, HepG2 cells:100.2 μM, COLO 320 cells:39.5 μM, BeWo cells:> 100 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: DLBCL cells LY1 and LY3 were treated with Vadimezan (0-300 µM) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK-8 assay. RESULTS: Vadimezan treatment decreased the viability of DLBCL cells in a dose-dependent manner, with IC50s of 177 μM and 165 μM for LY1 and LY3, respectively. [1] METHODS: Human lung cancer cells A549 were treated with Vadimezan (0.1-1 µM) for 24 h. The expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Vadimezan induced a significant increase in the cytoplasmic level of cytochrome c and the activation of caspase 3, which ultimately led to apoptosis and death of A549 cells. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, Vadimezan (20 mg/kg) and BMS1166 (250 µg/mL) were injected intraperitoneally into Balb/c nude mice bearing DLBCL tumor LY1 once daily for eight days. RESULTS: Vadimezan and BMS1166 acted at effective concentrations. The combination treatment significantly inhibited the growth of GCB-like DLBCL cells compared to monotherapy. [1] METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, Vadimezan (25,5,5,25 mg/kg; 25,0,0,25 mg/kg; 25,25,25,25 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally every three days to C57BL/6J mice bearing mouse mesothelioma AE17 for four doses. RESULTS: In group 1, 2/4 mice were cured, of which 2/4 showed long-term survival, but toxicity problems were observed. A better, less toxic response was observed in Group 2, with all four mice cured and showing long-term survival. In group 3, only 1 mouse was cured, but none showed long-term survival, possibly due to associated toxicity issues. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | DT-diaphorase activity and kinetic analysis of enzyme inhibition : Purified DT-diaphorase enzyme activity is assayed by measuring the reduction of cytochrome c at 550 nm on a Beckman DU 650 spectrophotometer. Each assay contains cytochrome c (70 μM), NADH (variable concentrations), purified DT-diaphorase (0.032 μg), and menadione (variable concentrations) in a final volume of 1 mL Tris–HCl buffer (50 mM, pH 7.4) containing 0.14% BSA. The reaction is started by the addition of NADH. Rates of reduction are calculated over the initial part of the reaction curve (30 seconds), and results are expressed in terms of μmol cytochrome c reduced/min/mg protein using a molar extinction coefficient of 21.1 mM?1 cm?1 for reduced cytochrome c. Enzyme assays are carried out at room temperature and all reactions are performed in triplicate. Inhibition of purified DT-diaphorase activity is performed by the inclusion of DMXAA (at various concentrations) in the reaction, and inhibition characteristics are determined by varying the concentration of NADH (constant menadione) or menadione (constant NADH) at several concentrations of inhibitor. Ki values are obtained by plotting 1/V against. The activity of DT-diaphorase in DLD-1 cells is determined by measuring the dicumarol-sensitive reduction of DCPIP at 600 nm. Briefly, DLD-1 cells in mid-exponential growth are harvested by scraping into ice-cold buffer (Tris–HCl, 25 mM, pH 7.4 and 250 mM sucrose) and sonicated on ice. Enzyme assay conditions are 2 mM NADH, 40 μM DCPIP, 20 μL of dicumarol (when required) in a final volume of 1 mL Tris–HCl (25 mM, pH 7.4) containing BSA (0.7 mg/mL). Results are expressed as the dicumarol-sensitive reduction of DCPIP using a molar extinction coefficient of 21 mM?1 cm?1. Protein levels are determined using the Bradford assay |
| Cell Research | DLD-1 human colon carcinoma and H460 human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells are routinely maintained as monolayer cultures in RPMI 1640 culture medium supplemented with foetal calf serum (10%), sodium pyruvate (2 mM), penicillin/streptomycin (50 IU mL?1/50 μg mL-1) and l-glutamine (2 mM). Chemosensitivity is assessed using the MTT assay and all assays are performed under aerobic conditions. Briefly, cells are plated into each well of a 96-well culture plate and incubated overnight in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Culture medium is completely removed from each well and replaced with medium containing a range of drug concentrations. In the case of menadione alone, the duration of drug exposure is 1 hour, after which the cells are washed twice with Hanks' balanced salt solution prior to the addition of 200 μL fresh RPMI 1640 medium to each well of the plate. In the case of DMXAA alone, the duration of drug exposure is 3 hours. Following a four-day incubation, cell survival is determined using the MTT assay. For combinations of DMXAA with menadione, cells are initially set up and a non-toxic (>95% cell survival) concentration of DMXAA is selected. Cells are then initially exposed to DMXAA (2 mM) for a period of 2 hours, following which the medium is removed and replaced with medium containing the inhibitor (DMXAA at a constant concentration of 2 mM) and menadione (at a range of drug concentrations). Following a further 7-hour incubation, cells are washed twice with Hanks' balanced salt solution prior to the addition of growth medium.(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | NSC 640488, DMXAA, ASA-404, 5,6-Dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic Acid |
| Molecular Weight | 282.29 |
| Formula | C17H14O4 |
| Cas No. | 117570-53-3 |
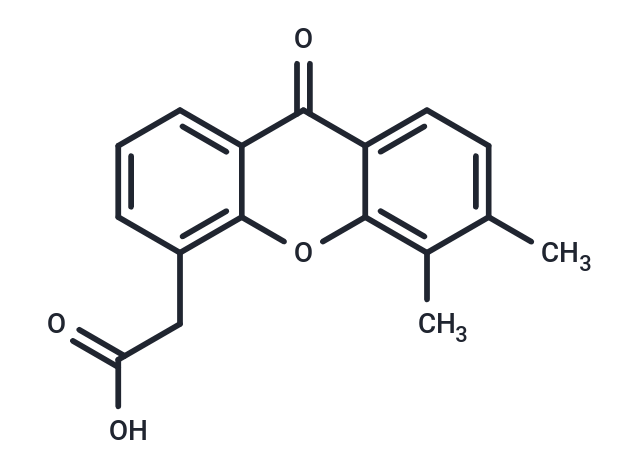
| Smiles | Cc1ccc2c(oc3c(CC(O)=O)cccc3c2=O)c1C |
| Relative Density. | 1.321g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 7.5 mg/mL (26.57 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 0.57 mg/mL (2.02 mM), Suspension. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.