 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Nilotinib (AMN107) is a Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor with oral activity. Nilotinib has antitumor activity and may be used for the treatment of Imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $35 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $50 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Nilotinib (AMN107) is a Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor with oral activity. Nilotinib has antitumor activity and may be used for the treatment of Imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). |
| Targets&IC50 | Abl (WT):15 nM (cell free), BJ cells:12.8 μM, K562 cells:0.015 μM, K562 cells:0.022 μM, HEK293 cells:0.5 μM, CHO cells:4.7 μM, H9C2 cells:21.33 μM, BaF3 cells:0.003 μM, A549 cells:6.63 μM, Bcr-Abl:260 nM, KU812 cells:1.8 nM, HCT116 cells:2.39 μM, Daoy cells:6 μM, KBM5 cells:12 nM, K562 cells:0.0039 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Ba/F3 cells expressing wild-type or mutant Bcr-Abl were treated with Nilotinib for 72 h, and cell viability was measured by methanethiosulfonate-based viability assay. RESULTS: Nilotinib inhibited the growth of cells expressing wild-type Bcr-Abl with 20-fold higher potency than imatinib (IC50:13 vs. 260 nmol/L). Similar improvements were maintained in all imatinib-resistant mutants tested except T315I. [1] METHODS: Melanoma cell line D04 was treated with Nilotinib (0.1-10 µM) for 3 h. Target protein expression levels were examined by Western Blot. RESULTS: Nilotinib stimulated robust MEK and ERK phosphorylation at concentrations as low as 100 nM. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To test the antitumor activity in vivo, Nilotinib (25 mg/kg) and PD184352 (25 mg/kg) were administered by gavage to Balb/cJ mice bearing Ba/F3 allografts of BCR-ABL or BCR-ABLT315I once daily for twenty days. RESULTS: Nilotinib strongly inhibited the growth of BCR-ABL tumors, but not PD184352, nor did PD184352 enhance the growth inhibitory activity of Nilotinib. In contrast, BCR-ABLT315I tumors were insensitive to both Nilotinib and PD184352, but these drugs synergistically inhibited tumor growth. [2] |
| Kinase Assay | Kinase assays using wild-type and mutant glutathione S-transferase (GST)–Abl fusion proteins (c-Abl amino acids 220-498) were done as described, with minor alterations. GST-Abl fusion proteins were released from glutathione-Sepharose beads before use; the concentration of ATP was 5 μmol/L. Immediately before use in kinase autophosphorylation and in vitro peptide substrate phosphorylation assays, GST-Abl kinase domain fusion proteins were treated with LAR tyrosine phosphatase according to the manufacturer's instructions. After 1-hour incubation at 30°C, LAR phosphatase was inactivated by addition of sodium vanadate (1 mmol/L). Immunoblot analysis comparing untreated GST-Abl kinase to dephosphorylated GST-Abl kinase was routinely done using phosphotyrosine-specific antibody 4G10 to confirm complete (>95%) dephosphorylation of tyrosine residues and c-Abl antibody CST 2862 to confirm equal loading of GST-Abl kinase. The inhibitor concentration ranges for IC50 determinations were 0 to 5,000 nmol/L (imatinib and AMN107) or 0 to 32 nmol/L (BMS-354825). The BMS-354825 concentration range was extended to 1,000 nmol/L for mutant T315I. These same inhibitor concentrations were used for the in vitro peptide substrate phosphorylation assays. The three inhibitors were tested over these same concentration ranges against GST-Src kinase and GST-Lyn kinase [1]. |
| Cell Research | Ba/F3 cell lines were plated in triplicate and incubated with escalating concentrations of imatinib, AMN107, or BMS-354825 for 72 hours. Proliferation was measured using a methanethiosulfonate-based viability assay. IC50 and IC90 values are reported as the mean of three independent experiments done in quadruplicate. The inhibitor concentration ranges for IC50 and IC90 determinations were 0 to 2,000 nmol/L (imatinib and AMN107) or 0 to 32 nmol/L (BMS-354825). The imatinib concentration range was extended to 6,400 nmol/L for mutants with IC50 >2,000 nmol/L. The BMS-354825 concentration range was extended to 200 nmol/L for mutant T315I [1]. |
| Animal Research | The GIST xenograft lines GK1X, GK2X and GK3X in nude mice were established from GIST patients as described in our previous study [10]. These xenograft lines were maintained by continual passage in BALB/cSLc-nu/nu mice. Mice bearing GK1X, GK2X and GK3X tumors (6–8 mice per group) were treated daily with vehicle or 40 mg/kg imatinib or nilotinib for 4 weeks. Tumor volume (TV) was determined from caliper measurements of tumor length (L) and width (w) according to the formula LW2/2. TV was determined every two to three days and on the day of evaluation. Mice were sacrificed and the percentage of tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was calculated as follows: TGI (%) ?=? [1– (mean of treatment group tumor volume on evaluation day – mean of treatment group tumor volume on day 1)/(mean of control group tumor volume on evaluation day – mean of control group tumor volume on day 1)]×100 [2]. |
| Synonyms | Tasigna, AMN107 |
| Molecular Weight | 529.52 |
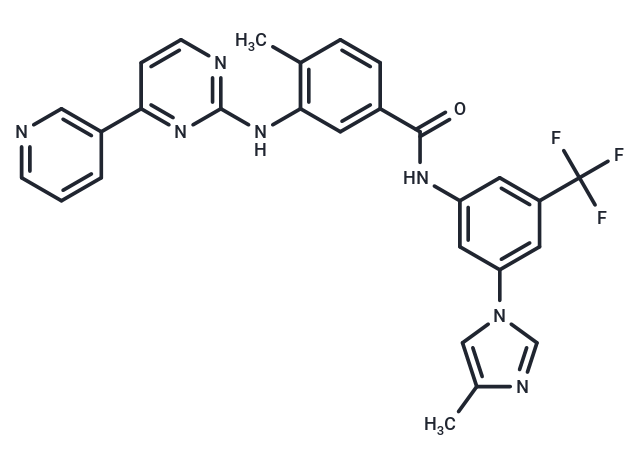
| Formula | C28H22F3N7O |
| Cas No. | 641571-10-0 |
| Smiles | C(F)(F)(F)C=1C=C(C=C(NC(=O)C2=CC(NC=3N=C(C=CN3)C=4C=CC=NC4)=C(C)C=C2)C1)N5C=NC(C)=C5 |
| Relative Density. | 1.36 g/cm3 |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 41.7 mg/mL (78.75 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2.6 mg/mL (4.91 mM), Suspension. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.