Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Neostibosan is an arsenic-containing parasitic agent. Due to the activity of arsenic on visceral L/Ashmaniasis, one of the pentvalent antimony, which is less toxic, is synthesized and has potential activity on tumor cells.
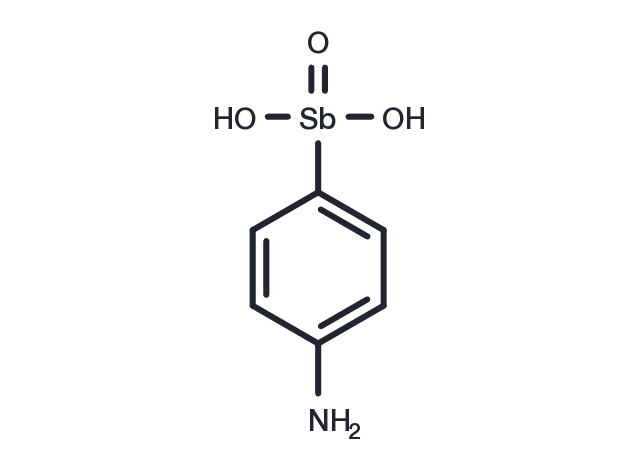
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | 6-8 weeks | $ 1,520.00 |
| Description | Neostibosan is an arsenic-containing parasitic agent. Due to the activity of arsenic on visceral L/Ashmaniasis, one of the pentvalent antimony, which is less toxic, is synthesized and has potential activity on tumor cells. |
| Synonyms | Stibanilic acid, 693B, Astaril, Ethylstibamine, p-Aminobenzenestibonic acid, Bayer 693 |
| Molecular Weight | 263.89 |
| Formula | C6H8NO3Sb |
| CAS No. | 554-76-7 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Neostibosan 554-76-7 Stibanilic acid 693B Astaril Ethylstibamine p-Aminobenzenestibonic acid Bayer 693 inhibitor inhibit
