Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


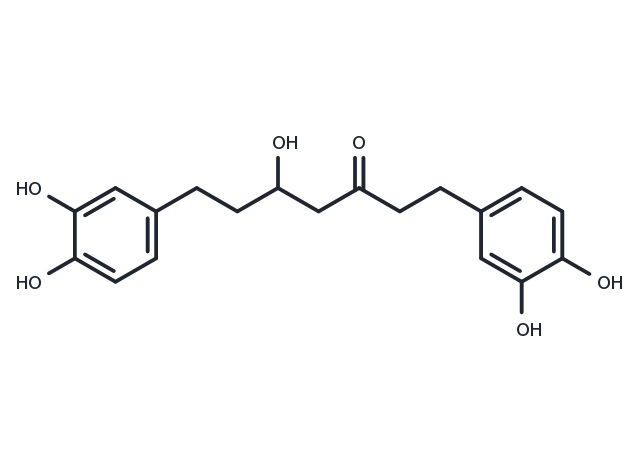
Hirsutanonol is a secondary metabolite from the bark of Alnus glutinosa. Hirsutanonol has potent antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities and exhibits an inhibition effect on mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. Hirsutanonol can be used for studies
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | Inquiry | $ 665.00 |

| Description | Hirsutanonol is a secondary metabolite from the bark of Alnus glutinosa. Hirsutanonol has potent antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities and exhibits an inhibition effect on mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. Hirsutanonol can be used for studies |
| In vitro | Hirsutanonol shows significant inhibitory effects on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in immortalized human breast epithelial MCF10A cells. Hirustenone and hirsutanonol show promising anti-filarial activity both in vitro and in vivo studies.Hirsutanonol shows potent cytotoxic activities against murine B16 melanoma cells and human SNU-C1 gastric cancer cells, it also has a chemoprotective effect on human lymphocyte DNA. Hirsutanonol (1 µg/mL) decreased the frequency of micronuclei by 63.6 %, exerting a much stronger effect than the synthetic protector amifostine (17.2 %, 1 µg/mL)[1]. |
| Source |
| Molecular Weight | 346.37 |
| Formula | C19H22O6 |
| CAS No. | 41137-86-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Hirsutanonol 41137-86-4 Immunology/Inflammation Microbiology/Virology Neuroscience COX Antifection inhibitor inhibit
