 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

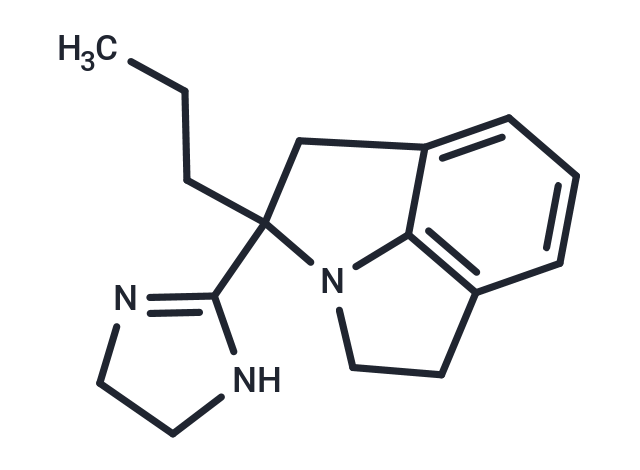
Deriglidole (SL 86-0715) is a peripheral adrenergic receptor antagonist that is a selective inhibitor of alpha2 receptors. Deriglidole inhibits colistin and Idazoxan but does not show activity against prazosin and rat cortical and human platelet α2-adrenergic receptors.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $276 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $636 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $852 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $1,260 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $475 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Deriglidole (SL 86-0715) is a peripheral adrenergic receptor antagonist that is a selective inhibitor of alpha2 receptors. Deriglidole inhibits colistin and Idazoxan but does not show activity against prazosin and rat cortical and human platelet α2-adrenergic receptors. |
| In vitro | Deriglidole is a specific inhibitor of α2-receptors. Deriglidole inhibits the binding of [3H] clonidine and [3H] imidazole x, while showing no inhibitory effect on the binding of [3H] prazosin to rat cortex and human platelet α2-adrenergic receptors. Furthermore, it demonstrates greater effectiveness than idazolide in selectively targeting peripheral receptors.[1] |
| In vivo | In mouse pancreatic beta-cells that both deriglidole and SL86.0714 inhibit ATP-sensitive K+ channel with similar potency whereas alpha2-adrenoceptors are blocked only by deriglidole. In diabetic rats, SL84.0418 and deriglidole (10 mg/kg i.p.) fully normalized glucose tolerance whereas SL86.0714 and tolbutamide only slightly improved it. Five min after deriglidole administration in mice a marked and short lasting rise in insulin levels was observed, followed by a progressive reduction of glycemia.[2] |
| Synonyms | SL 86-0715 |
| Molecular Weight | 255.36 |
| Formula | C16H21N3 |
| Cas No. | 122830-14-2 |
| Smiles | C(CC)C1(N2C=3C(C1)=CC=CC3CC2)C=4NCCN4 |
| Relative Density. | 1.27 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Pure form: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 32.5 mg/mL (127.27 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.