Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Conivaptan hydrochloride (Vaprisol) is an orally active vasopressin V2 and V1A receptor antagonist, used in the therapy of hypervolemic hyponatremia and euvolemic.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $37 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $59 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $132 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $238 | In Stock | - | |
| 100 mg | $397 | In Stock | - | |
| 200 mg | $597 | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $65 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Conivaptan hydrochloride (Vaprisol) is an orally active vasopressin V2 and V1A receptor antagonist, used in the therapy of hypervolemic hyponatremia and euvolemic. |
| Targets&IC50 | V1a receptor(rat liver):0.48nM(Ki), V2 receptor (rat kidney):3.04 nM(Ki) |
| In vivo | Conivaptan administered intravenously at doses of 0.03, 0.1, and 0.3 mg/kg increases urine volume and decreases urine osmolality in a dose-dependent manner in both myocardial infarction and sham-operated rats. In myocardial infarction rats, a dose of 0.3 mg/kg notably lowers right ventricular systolic pressure, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, reduces lung/body weight ratio, and right atrial pressure, while significantly enhancing dP/dt(max)/left ventricular pressure. Additionally, conivaptan acutely augments urine volume, reduces osmolality, and at study conclusion, cirrhotic rats treated with the V(1a)/V(2)-AVP receptor antagonist exhibit neither hyponatremia nor hypoosmolality. It also normalizes sodium urine volume without impacting creatinine clearance or arterial pressure. At dosages ranging from 0.01 to 0.1 mg/kg i.v., conivaptan demonstrates a dose-dependent diuretic effect in dogs, effectively inhibits vasopressin-induced pressor effects, and at 0.1 mg/kg, substantially blocks vasoconstriction from exogenous vasopressin. Furthermore, at 0.1 mg/kg i.v., it significantly enhances cardiac function in dogs with congestive heart failure as demonstrated by increases in left ventricular dP/dtmax, cardiac output, and stroke volume, alongside significant reductions in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and total peripheral vascular resistance. |
| Synonyms | YM 087, Vaprisol, Conivaptan HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 535.04 |
| Formula | C32H26N4O2·HCl |
| Cas No. | 168626-94-6 |
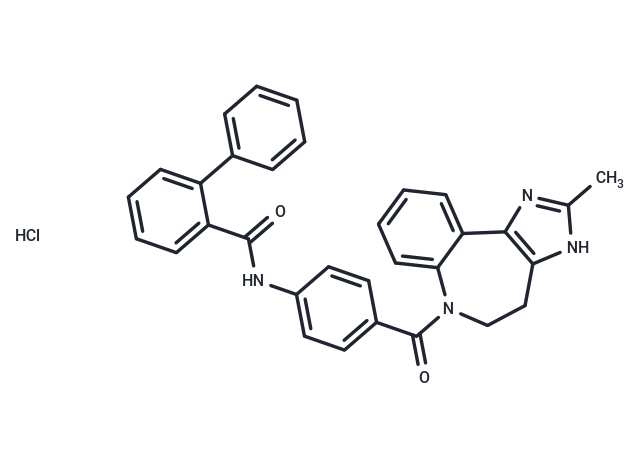
| Smiles | Cl.Cc1nc-2c(CCN(C(=O)c3ccc(NC(=O)c4ccccc4-c4ccccc4)cc3)c3ccccc-23)[nH]1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 7 mg/mL (13.08 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 99 mg/mL (185.03 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 3.3 mg/mL (6.17 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.