Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Batabulin sodium (T138067 sodium) is an antitumor agent, which covalently and selectively modifies the β-tubulin isotypes, thereby disrupting microtubule polymerization. Batabulin sodium affects cell morphology and leads to cell-cycle arrest ultimately induces apoptotic cell death [1].
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | 5 days | $ 68.00 | |
| 5 mg | 5 days | $ 148.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | 5 days | $ 144.00 |
| Description | Batabulin sodium (T138067 sodium) is an antitumor agent, which covalently and selectively modifies the β-tubulin isotypes, thereby disrupting microtubule polymerization. Batabulin sodium affects cell morphology and leads to cell-cycle arrest ultimately induces apoptotic cell death [1]. |
| In vitro | Treatment with Batabulin (T138067; 30-300 nM; 24-48 hours) in MCF7 cells results in cell-cycle arrest at the G2/M boundary, evidenced by 25-30% of cells displaying tetraploid (4n) DNA content, and induces apoptosis, with 25-30% of cells becoming apoptotic within 24-48 hours, and 50-80% after 48-hour exposure to 100 nM. Batabulin selectively and covalently binds to the β1, β2, and β4 isotypes of β-tubulin at the conserved Cys-239 residue, disrupting microtubule polymerization, leading to cytoskeletal collapse, altered cell shape, and increased chromosomal ploidy. Cell cycle and apoptosis analyses further substantiate these effects, highlighting Batabulin's potential mechanism of action through perturbation of the cell cycle and induction of apoptosis in MCF7 cells [1]. |
| In vivo | Batabulin treatment (T138067; 40 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; once per week on days 5, 12, and 19) significantly impaired the growth of drug-sensitive CCRF-CEM tumors in a study involving male athymic nude mice (nu/nu; 6-8 weeks old, 20-25 g) that were injected with CCRF-CEM cells [1]. The study utilized a dosage of 40 mg/kg administered through intraperitoneal injection once per week on specified days, leading to the observed result of hindered tumor growth. |
| Molecular Weight | 393.24 |
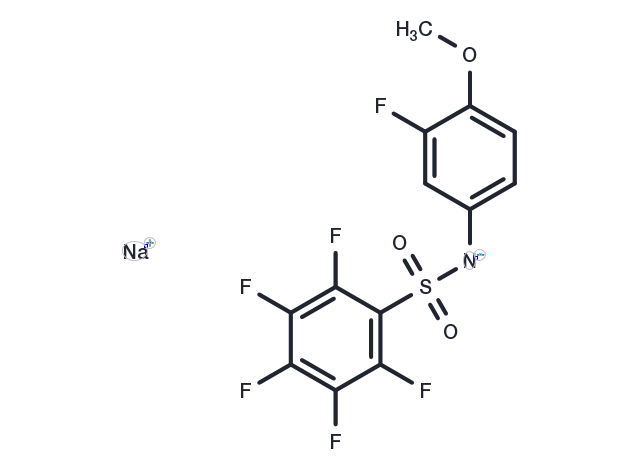
| Formula | C13H6F6NNaO3S |
| CAS No. | 195533-98-3 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Batabulin sodium 195533-98-3 inhibitor inhibit
