Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


BF844 is a chemical compound that demonstrates the ability to mitigate hearing loss in individuals with Usher Syndrome Type III (USH3) caused by the CLRN1 mutation (specifically N48K). One of its mechanisms of action is the transportation of CLRN1 N48K to the plasma membrane. In vivo studies have shown that BF844 significantly preserves hearing [1].
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | 6-8 weeks | $ 1,520.00 | |
| 50 mg | 6-8 weeks | $ 1,980.00 | |
| 100 mg | 6-8 weeks | $ 2,500.00 |
| Description | BF844 is a chemical compound that demonstrates the ability to mitigate hearing loss in individuals with Usher Syndrome Type III (USH3) caused by the CLRN1 mutation (specifically N48K). One of its mechanisms of action is the transportation of CLRN1 N48K to the plasma membrane. In vivo studies have shown that BF844 significantly preserves hearing [1]. |
| In vitro | BF844 (compound 3), at a concentration of 0.846 μM, significantly inhibits HSP60 activity, achieving an 87.07±27.70% reduction, and shows moderate inhibition towards HSP90, with a 40.06±19.10% decrease [1]. At a higher concentration of 2.90 μM and after 24 hours of treatment, BF844 induces approximately 6% of the total CLRN1 N48K mutation to reach the plasma membrane in C1, D1, D6 cells [1]. Furthermore, the same conditions (2.90 μM; 24 hours) lead to an increase in non-glycosylated CLRN1 levels, with effective transportation of this form to the plasma membrane in C1 and D1 cells [1]. |
| In vivo | BF844 demonstrates effective penetration into the retina and cochlea when administered in vivo. At a dosage of 10 mg/kg via intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection, BF844 notably preserves hearing in Tg;KI/KI mice. In juvenile mice, dosages of 3 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg (corresponding to post-natal day 6 and day 20 mice, respectively) were administered i.p., revealing area under curve (AUC) values of 1.76 μM.h and 1.98 μM.h. For P30 Tg;KI/KI C57BL/6J mice given 30 mg/kg i.p. daily from P30 to P45, hearing was significantly preserved, with the median threshold of sound intensity at 57.5–67.5 dB SPL, indicating a thousand-fold increase in sensitivity compared to untreated controls at P55. In a separate study, P10 Tg;KI/KI C57BL/6J mice receiving an initial dose of 10 mg/kg i.p. every other day, with doses increasing to 20 mg/kg by P28 and then to 30 mg/kg daily from P30 to P45, showed median thresholds of sound intensity that were 55, 42.5, and 37.5 dB SPL lower at frequencies of 8, 16, and 32 kHz, respectively, at P55. |
| Molecular Weight | 378.85 |
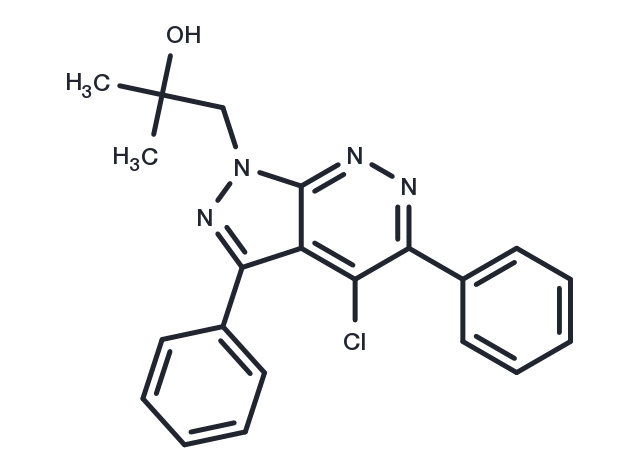
| Formula | C21H19ClN4O |
| CAS No. | 1404506-35-9 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
BF844 1404506-35-9 inhibitor inhibit
