Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

5'-N-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA), an agonist of the Adenosine receptor, increases cerebral extravasation of fluorescein and low molecular weight dextran independent of blood-brain barrier modulation.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $51 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $146 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $217 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $57 | In Stock |
| Description | 5'-N-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA), an agonist of the Adenosine receptor, increases cerebral extravasation of fluorescein and low molecular weight dextran independent of blood-brain barrier modulation. |
| In vitro | In vitro cultures of an Epo producing hepatocellular carcinoma (Hep3B) cell line with 5'-N-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (> or = 10(-6) M) for 20 hours under hypoxic conditions (1% O2) produced significant increases in medium levels of Epo when compared with hypoxia controls. Hepatocellular carcinoma cells treated with 5'-N-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine at a concentration range of 10(-7) M to 5 x 10(-5) M for one hour in a hypoxic atmosphere also had significantly higher cAMP levels than that of hypoxia controls. Scatchard analyses of [3H]5'-N-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine binding to membrane preparations of hepatocellular carcinoma cells showed low affinity binding sites with a dissociation-constant (Kd) of 0.44 microM and a binding capacity of 863 fmol/mg protein. Suggest that the increase in Epo production in response to 5'-N-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine under hypoxic conditions can be attributed, at least in part, to stimulation of adenosine A2 receptors which is coupled to adenylyl cyclase activation[1]. |
| In vivo | 5'-N-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine, an adenosine analogue, on erythropoietin (Epo) production. 5'-N-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (0.05 and 0.1 mumol/kg i.v.) produced significant increases in serum Epo levels (368.8 +/- 56.1 and 384.6 +/- 45.9 mU/ml, respectively) in exhypoxic polycythemic mice after a four hour exposure to hypoxia when compared with hypoxia controls (133.2 +/- 18.2 mU/ml). The hypoxic kidney Epo levels were 46.4 +/- 13.4 mU/kg kidney which were significantly higher than normoxic kidney Ep levels (< 1.24 mU/kg kidney). Theophylline (20 mg/kg i.p.), an adenosine receptor antagonist, significantly inhibited the stimulatory effects of 5'-N-Ethylcarboxamidoadenosine on serum Epo levels[1]. |
| Cell Research | A human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (Hep3B) was employed to determine the in vitro effects of NECA on Epo production and cAMP accumulation. Hep3B cells were carried in a monolayer cell culture and maintained in 75 cm^2 Corning culture flasks containing Eagle's minimal essential medium (MEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (PBS), 0.1 m nonessential amino acids, 1 m sodium pyruvate, 100 U/ml penicillin G, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin in a humidified atmosphere of 5% C02/95% air at 37℃. The culture medium was replaced every two days. Cells were detached with trypsin and aliquots of 2.5 x 10^5 viable cells (determined by trypan blue dye exclusion) were transferred to 24 multi-well plates. Each experiment was carried out with low density cells before they reached confluency. The cells were incubated with NECA in concentrations of 1O^9 M to 5 x l0^-5 M in the presence of 1 U/ml adenosine deaminase (ADA) under hypoxic conditions (1% 02, 5% C02, and 94% N2) for 20 hours following 24 hour preincubation in a normoxic atmosphere. At the end of the incubation period, the supernatant was harvested and frozen at -70℃ prior to Epo RIA. The multiple-range test of Duncan was used for the comparison of the several in vitro treatment groups compared with controls[1]. |
| Alias | NECA |
| Molecular Weight | 308.29 |
| Formula | C12H16N6O4 |
| Cas No. | 35920-39-9 |
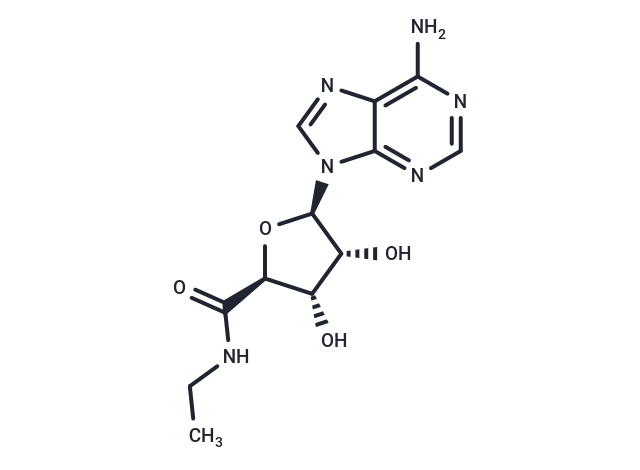
| Smiles | CCNC(=O)[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)n1cnc2c(N)ncnc12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.87 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 150 mg/mL (486.55 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.