Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
1-Naphthohydroxamic acid (Compound 2) is a potent and selective HDAC8 inhibitor with an IC50 of 14 μM, demonstrating greater selectivity for HDAC8 than class I HDAC1 and class II HDAC6 (IC50 >100 μM). It does not increase global histone H4 acetylation or reduce total intracellular HDAC activity but can induce tubulin acetylation[1][2].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $29 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $58 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $116 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $223 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $333 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $478 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $34 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | 1-Naphthohydroxamic acid (Compound 2) is a potent and selective HDAC8 inhibitor with an IC50 of 14 μM, demonstrating greater selectivity for HDAC8 than class I HDAC1 and class II HDAC6 (IC50 >100 μM). It does not increase global histone H4 acetylation or reduce total intracellular HDAC activity but can induce tubulin acetylation[1][2]. |
| Targets&IC50 | HDAC1:>100 μM, HDAC6:>100 μM, HDAC8:14 μM |
| In vitro | 1-Naphthohydroxamic acid (compound 2; 20-40 μM; 0-144 hours; BE(2)-C, SK-N-BE(2), and SH-SY5Y cells) reduces cell numbers in a concentration-dependent manner [2]. It decreases clone formation in soft agar in a similar manner [2]. In HeLa and HEK293 cells treated with 1-Naphthohydroxamic acid (compound 2; 0.8 μM, 4 μM, 20 μM, or 100 μM), only tubulin becomes hyperacetylated [1]. At concentrations within its in vitro IC50 against HDAC8, 1-Naphthohydroxamic acid (compound 2) reduces cell density and induces outgrowth of neurofilament-positive neurite-like structures. |
| In vivo | 1-Naphthohydroxamic acid has the maximum tolerable doses at 50?mg/kg per day. At these concentrations, neither body weight nor blood parameters are critically changed[3]. Dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) of 1-Naphthohydroxamic acid (compound 2; 0-40 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 10 day; NMRI Foxn1 nude mice) include weight loss and signs of liver toxicity, as evidenced by elevated plasma liver enzymes and detection of necrotic areas on histological liver examination. Pharmacokinetic studies after intraperitoneal administration of the inhibitors identified the half-life of 1-Naphthohydroxamic acid to be ~15?min, with a plasma peak concentration of ~30?μM[3]. |
| Molecular Weight | 187.19 |
| Formula | C11H9NO2 |
| Cas No. | 6953-61-3 |
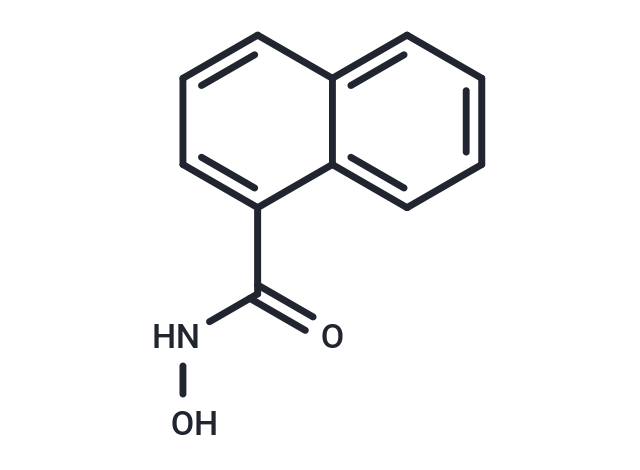
| Smiles | ONC(=O)c1cccc2ccccc12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.291g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 125 mg/mL (667.77 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.