 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Ganciclovir (BW 759) hydrate is a nucleoside analogue that is an orally active antiviral agent with anti-cytomegalovirus activity. Ganciclovir hydrate is also active against members of the herpes group and some other DNA viruses in vitro. Ganciclovir hydrate inhibits the replication of human herpes viruses (HSV 1 and 2, CMV) and adenovirus serotypes 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 19, 22 and 28 in vitro. Ganciclovir hydrate also has an IC 50 of 5.2 μM against feline herpesvirus type-1 ( FHV-1 ) and can diffuse into the brain [1] [2] [3].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $1,520 | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks | |
| 50 mg | $1,980 | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks | |
| 100 mg | $2,500 | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks |
| Description | Ganciclovir (BW 759) hydrate is a nucleoside analogue that is an orally active antiviral agent with anti-cytomegalovirus activity. Ganciclovir hydrate is also active against members of the herpes group and some other DNA viruses in vitro. Ganciclovir hydrate inhibits the replication of human herpes viruses (HSV 1 and 2, CMV) and adenovirus serotypes 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 19, 22 and 28 in vitro. Ganciclovir hydrate also has an IC 50 of 5.2 μM against feline herpesvirus type-1 ( FHV-1 ) and can diffuse into the brain [1] [2] [3]. |
| Targets&IC50 | FHV-1:5.2 μM |
| In vitro | Ganciclovir (BW 759), an acyclic deoxyguanosine analog akin to acyclovir, demonstrates enhanced efficacy against CMV, requiring a median concentration of 2.15 μM to inhibit viral replication by 50%, compared to acyclovir's 72 μM [4]. Its mechanism of action involves the selective and potent inhibition of viral DNA polymerase by ganciclovir-5'-triphosphate (ganciclovir-TP), effectively halting CMV DNA replication. Metabolism of ganciclovir to its active triphosphate form is facilitated by three key cellular enzymes: deoxyguanosine kinase, activated in CMV-infected cells; guanylate kinase; and phosphoglycerate kinase [5]. |
| In vivo | Ganciclovir (BW 759), administered at a dosage of 50 mg/kg intraperitoneally (i.p.) twice daily for a total of five injections, has been found to significantly reduce the levels of white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets in newborn mice, while also demonstrating the capacity to penetrate the brain and perilymphatic space of the inner ear [3]. Furthermore, a dosage regimen of 1-80 mg/kg, administered intrahippocampally (i.h.) once daily for 5 days, effectively delays the onset of wasting syndrome and mortality in mice infected with murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV), with non-inbred Oncins France 1 (OF1) mice and albino rats (non-immunized for MCMV) serving as the animal models [3, 6]. Pharmacokinetic studies have revealed that in adult rats, Ganciclovir achieves equivalent concentrations in the cochlea and blood, exhibits transplacental diffusion in gestating mice with a fetal-to-maternal blood ratio of 0.5, and demonstrates a time-dependent concentration profile in the plasma of both newborn and adult mice. Specifically, newborn mice exhibited peak plasma concentrations at 2 hours post-injection, followed by a gradual decline, whereas in adult mice, peak concentration occurred at 1 hour but became undetectable by 2 hours post-injection. Additionally, in an experimental setup involving female SCID mice inoculated with MCMV, Ganciclovir administered subcutaneously at doses ranging from 0, 1, 10, 80 to 160 mg/kg once daily for 5 days, was found to delay disease progression and mortality in a dose-dependent manner up to 80 mg/kg per day, with a dose of 160 mg/kg per day associated with reversible side-effects [6]. |
| Molecular Weight | 273.249 |
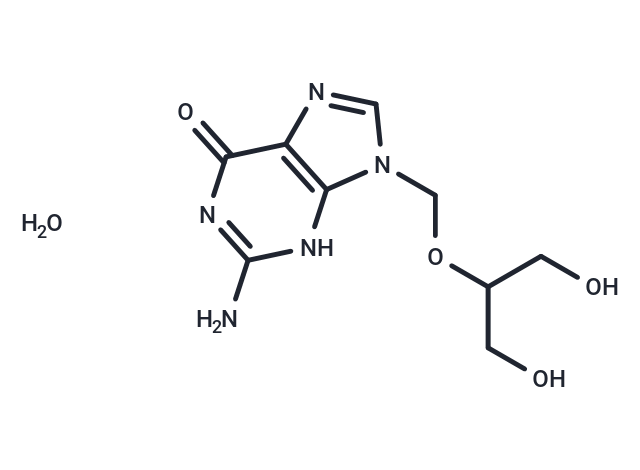
| Formula | C9H15N5O5 |
| Cas No. | 1359968-33-4 |
| Smiles | O.Nc1nc(=O)c2ncn(COC(CO)CO)c2[nH]1 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.