 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

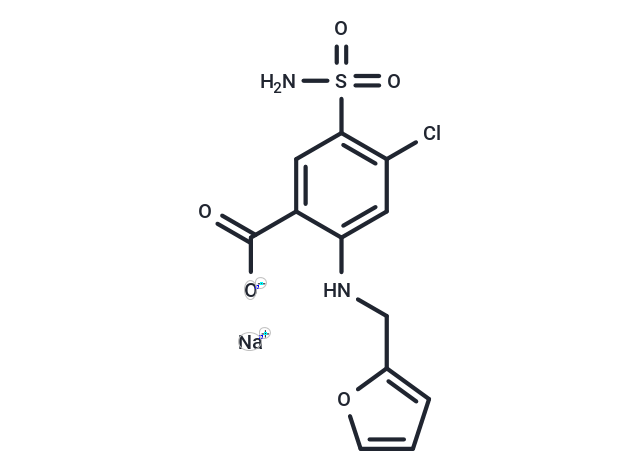
Furosemide sodium (Frusemide Sodium) is a potent and orally active inhibitor of Na+/K+/2Cl- (NKCC) cotransporter, NKCC1 and NKCC2. Furosemide sodium is also a GABAA receptors antagonist and displays 100-fold selectivity for α6-containing receptors than α1-containing receptors. Furosemide sodium acts as a loop diuretic and used for the study of congestive heart failure, hypertension and edema.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $29 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $79 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Furosemide sodium (Frusemide Sodium) is a potent and orally active inhibitor of Na+/K+/2Cl- (NKCC) cotransporter, NKCC1 and NKCC2. Furosemide sodium is also a GABAA receptors antagonist and displays 100-fold selectivity for α6-containing receptors than α1-containing receptors. Furosemide sodium acts as a loop diuretic and used for the study of congestive heart failure, hypertension and edema. |
| Targets&IC50 | NKCC:, GABAA receptor: |
| In vitro | Furosemide sodium, at a concentration of 500 µM administered over 72-96 hours, significantly alters the proliferation rates of MKN45 cells, a poorly differentiated human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line, while exhibiting no impact on MKN28 cells, a moderately differentiated counterpart, with MKN45 cells displaying a higher growth rate [4]. Additionally, exposures to Furosemide sodium at concentrations of 10 µM, 30 µM, and 100 µM for 45 minutes substantially reduce cation channel activity and intracellular Ca(2+) levels in human erythrocytes from healthy individuals. Conversely, Tert-butylhydroperoxide increases non-selective cation channel activity and intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations, promoting cell membrane scrambling, which is notably mitigated by Furosemide sodium [5]. |
| In vivo | Furosemide sodium (intraperitoneal injection; 100 mg/kg; single dose) is administered following kanamycin (KM) (1000 mg/kg) to establish a deaf mouse model in C57BL/6 mice. This regimen leads to the evaluation of hearing loss and cochlear hair cell damage on days 1, 2, and 3 post-injection. Marked deterioration in hearing is observed as early as the next day (Day-1 group), with the morphology of outer hair cells (OHCs) within the apical, middle, and basal turns of the cochlea becoming disorganized by day 3[1]. |
| Synonyms | Lasix, Frusemide Sodium |
| Molecular Weight | 352.73 |
| Formula | C12H10ClN2NaO5S |
| Cas No. | 41733-55-5 |
| Smiles | O=C([O-])C1=CC(S(=O)(N)=O)=C(Cl)C=C1NCC2=CC=CO2.[Na+] |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (708.76 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 4 mg/mL (11.34 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.