 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

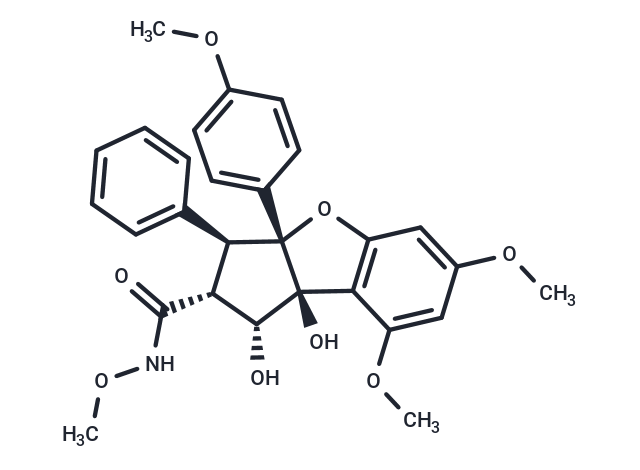
CR-1-31-B, a synthetic rocaglate, acts as a highly potent inhibitor of eIF4A. By disrupting the interaction between eIF4A and RNA, it effectively obstructs the initiation phase of protein synthesis. Specifically, CR-1-31-B interferes with the association between Plasmodium falciparum eIF4A (PfeIF4A) and RNA. Additionally, CR-1-31-B induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma and gallbladder cancer cells [4].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $1,298 | 8-10 weeks | 8-10 weeks | |
| 10 mg | $1,850 | 8-10 weeks | 8-10 weeks | |
| 25 mg | $3,680 | 8-10 weeks | 8-10 weeks |
| Description | CR-1-31-B, a synthetic rocaglate, acts as a highly potent inhibitor of eIF4A. By disrupting the interaction between eIF4A and RNA, it effectively obstructs the initiation phase of protein synthesis. Specifically, CR-1-31-B interferes with the association between Plasmodium falciparum eIF4A (PfeIF4A) and RNA. Additionally, CR-1-31-B induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma and gallbladder cancer cells [4]. |
| In vitro | CR-1-31-B (100 nM; 24 hours) inhibits MUC1-C translation in EGF-stimulated MCF-10A cells and decreases MUC1-C abundance in MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells. It sensitizes gallbladder cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by downregulating c-FLIP at the translational level. Neuroblastoma (NB) cell lines show decreased viability, increased apoptosis, and altered cell cycle distribution when treated with CR-1-31-B (24-72 hours), clamping eIF4A and eIF4F onto mRNA to block translation. Additionally, CR-1-31-B (100 nM; 5 hours) enhances reverse glutamine metabolism in pancreatic cancer cells. In viability assays, SH-SY5Y cells and Kelly cells treated with concentrations of 0.1-100 nM for 24-72 hours exhibit significant decreases in viability, with IC50 values of 20 nM for SH-SY5Y and 4 nM for Kelly cells at 48 hours. Apoptosis analysis reveals that CR-1-31-B induces apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells (10, 20, 50 nM) and Kelly cells (1, 5, 10 nM) over 24-72 hours. |
| In vivo | CR-1-31-B, administered intraperitoneally (IP) at a dosage of 2 mg/kg in 60 μL of olive oil once every two days over 28 days, effectively reduces growth and induces TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in gallbladder cancer cells (GBC) within a BALB/c nude mouse model[2]. Additionally, at a lower dosage of 0.2 mg/kg IP daily for 7 days in a murine orthotopic transplant model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, CR-1-31-B significantly inhibits protein synthesis and tumor growth in pancreatic cancers[5]. |
| Molecular Weight | 507.539 |
| Formula | C28H29NO8 |
| Cas No. | 1352914-52-3 |
| Smiles | CONC(=O)[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@]2(O)c3c(O[C@]2([C@@H]1c1ccccc1)c1ccc(OC)cc1)cc(OC)cc3OC |
| Relative Density. | 1.356 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.