 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

AVE 0991, a nonpeptide analog of angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)], is an orally active Mas agonist with inhibitory effects on [125I]-Ang-(1-7) binding to bovine aortic endothelial cell membranes, and inhibits astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease by enhancing autophagy.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $82 | - | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $147 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $239 | In Stock | - | |
| 25 mg | $459 | 5 days | 5 days | |
| 50 mg | $718 | 10-14 weeks | 10-14 weeks | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $189 | - | In Stock |
| Description | AVE 0991, a nonpeptide analog of angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)], is an orally active Mas agonist with inhibitory effects on [125I]-Ang-(1-7) binding to bovine aortic endothelial cell membranes, and inhibits astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease by enhancing autophagy. |
| Targets&IC50 | Ang (1-7) receptor:21±35 nM |
| In vitro | AVE 0991 is a nonpeptide compound that elicits effects on the endothelium similar to Angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)]. AVE 0991 and unlabeled Ang-(1-7) compete for high-affinity binding of [125I]-Ang-(1-7) to bovine aortic endothelial cell membranes with IC50s of 21±35 and 220±280 nM, respectively. The peak concentrations of NO and O2- release induced by AVE 0991 sodium salt and Ang-(1-7) (both at 10 μM) show no significant difference (NO: 295±20 and 270±25 nM; O2-: 18±2 and 20±4 nM); however, the amount of bioactive NO released is approximately 5 times higher for AVE 0991 compared to Ang-(1-7) [1]. |
| In vivo | In wild-type (WT) mice, the administration of AVE 0991 at a dose of 0.58 nmol/g leads to a significant reduction in water diuresis compared to vehicle-treated mice (0.06±0.03 mL versus 0.27±0.05; n=9 for each group; P<0.01). This antidiuretic effect of AVE 0991 is accompanied by an increase in urine osmolality (1669±231.0 mOsm/KgH2O versus 681.1±165.8 mOsm/KgH2O in vehicle-treated mice; P<0.01).The genetic deletion of Mas, a receptor associated with the effects of AVE 0991, eliminates the antidiuretic impact of AVE 0991 during water loading (0.37±0.10 mL [n=9] versus 0.27±0.03 mL [n=11] in AVE 0991-treated mice). Similar to observations in C57BL/6 mice, the administration of AVE 0991 (0.58 nmol/g) in water-loaded Swiss mice also results in a significant reduction in urinary volume compared to vehicle-treated animals (0.13±0.05 mL [n=16] versus 0.51±0.04 mL [n=40]; P<0.01).Furthermore, a one-week treatment with AVE-0991 induces a notable decrease in perfusion pressure (56.55±0.86 vs. 68.73±0.69 mmHg in vehicle-treated rats) and an increase in systolic tension (11.40±0.05 vs. 9.84±0.15 g in vehicle-treated rats). Additionally, there is an elevation in the rate of tension rise (+dT/dt; 184.30±0.50 vs. 155.20±1.97 g/s in vehicle-treated rats) and the rate of tension fall (dT/dt; 179.60±1.39 vs. 150.80±2.42 g/s in vehicle-treated rats). A slight increase in heart rate (HR) is also observed (220.40±0.71 vs. 214.20±0.74 beats/min in vehicle-treated rats) [4]. |
| Kinase Assay | Briefly, 100 μg of membranes from primary cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs, passage 1) are incubated in a total volume of 200 μL for 45 minutes at 25°C in HEPES-buffered saline (10 mM HEPES, 0.1 M NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2) containing 0.2% BSA and protease inhibitor cocktail Complete. Saturable binding of [125I]-Ang-(1-7) is calculated by subtracting nonspecific binding (40% to 50%), determined in the presence of 10 μM unlabeled Ang-(1-7) from total binding. Competition experiments with increasing concentrations of AVE 0991 and unlabeled Ang-(1-7) are performed in the presence of 10 nM [125I]-Ang-(1-7). Assays are terminated by vacuum filtration (≤15 mm Hg) over filters (0.65 μm, Opak 96-well plates) presoaked with 1% BSA. The filters are washed 3 times with each 100 μL of PBS (50 mM, NaHPO4 and 0.15 M NaCl, pH 7.2). Radioactivity on dried filters is quantified with a gamma counter [1]. |
| Cell Research | COS cells and CHO cells are stably transfected with rat Mas cDNA driven by a cytomegalovirus promoter and selected by neomycin. 125I-Ang-(1-7) (0.5×10^-9 mol/L) is incubated in 24-well plates for 60 minutes at 4°C in 0.3 mL of serum-free medium (DMEM) supplemented with 0.2% BSA, 0.005% bacitracin, 0.1 mol/L PMSF, and 0.5 mol/L orthophenanthroline with Mas-transfected COS cells in the presence or absence of AVE 0991 (AVE, 10-10 to -5 mol/L). After 2 ishes with ice-cold serum-free DMEM, cells are disrupted with 0.1% Triton X-100. Bound radioactivity is measured in a gamma counter. Binding of rhodamine-Ang-(1-7) in Mas-transfected CHO cells is performed under similar conditions using 2×10^-9 mol/L rhodamine-labeled-Ang-(1-7) in the presence or absence of AVE (10^-6 mol/L), CV11974 (10^-6 mol/L), or PD123319 (10^-6 mol/L). NSB is determined in the presence of 10-6 mol/L Ang-(1-7) [1]. |
| Animal Research | Swiss male mice, Mas-KO (Mas-/-) male mice on the pure genetic background C57BL/6, and WT C57BL/6 control mice (Mas+/+) are used. Water diuresis is induced by intraperitoneal water injection (0.05 mL/g of body weight [BW]) in conscious mice. Drugs are administered in the same injection with water load at prefixed volumes (0.01 mL/g BW). In the first set of experiments, WT mice (C57BL/6, control group) or Mas-KO mice are treated with: (1) 0.58 nmol/g AVE 0991 (n=9, control; n=11, Mas-KO mice); or (2) vehicle for AVE 0991 (10 μM KOH, 0.01 mL/g; n=9, control; n=9, Mas-KO). In the second set, Swiss mice are treated with: (1) vehicle (n=36); (2) 0.58 nmol/g AVE 0991 (n=16); (3) 46 pmol/g Ang-(1-7) antagonist A-779 (n=4); (4) 2 nmol/g losartan or valsartan (n=5); (5) 2 nmol/g AT2 receptor antagonists PD123319 or PD123177 (n=9); (6) AVE 0991 combined with A-779; (7) AVE 0991 combined with losartan or valsartan (n=4 for each); (8) or AVE 0991combined with PD123319 (n=5) or PD123177 (n=4). The urinary volume is measured for 60 minutes after water loading, and urine samples are obtained to determine the osmolality [2]. Male Wistar rats weighing 250-300 g are used. Rats are treated either with AVE-0991 (1 mg/kg, n=9) or vehicle (0.9% NaCl, n=11) administered orally by gavage. At the end of the 7 day period of AVE-0991 treatment, the animals are decapitated 10-15 min after intraperitoneal injection of 400 IU of heparin. After the thorax is opened, the heart is carefully dissected, removed from the thoracic cavity, and placed in a plate containing ice-cold Krebs-Ringer solution (KRS) to attenuate any potential cardiac damage during dissection of aorta artery [3]. |
| Molecular Weight | 580.72 |
| Formula | C29H32N4O5S2 |
| Cas No. | 304462-19-9 |
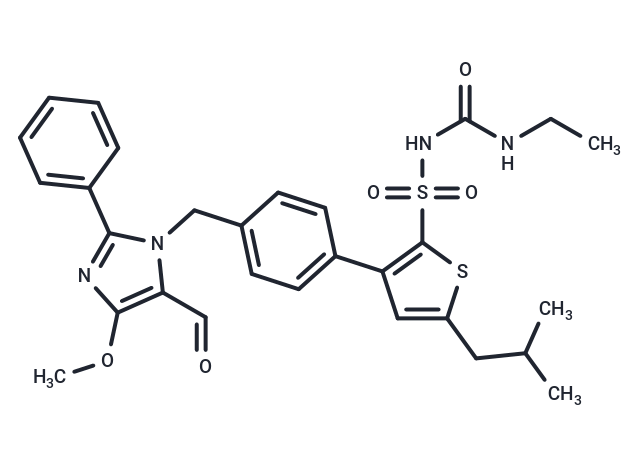
| Smiles | CCNC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)c1sc(CC(C)C)cc1-c1ccc(Cn2c(C=O)c(OC)nc2-c2ccccc2)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.31 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: <0.1 mg/mL (Insoluble) DMSO: 30 mg/mL (51.66 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (3.44 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.