Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Streptozotocin (Streptozocin, NSC-85998) is an antibiotic that enters pancreatic β-cells via the glucose transporter (GLUT2) and induces DNA methylation, leading to β-cell apoptosis. It is toxic to insulin-producing cells and commonly used to establish diabetic animal models. This product is unstable in solution and is recommended to be prepared freshly before use.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $73 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $105 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Streptozotocin (Streptozocin, NSC-85998) is an antibiotic that enters pancreatic β-cells via the glucose transporter (GLUT2) and induces DNA methylation, leading to β-cell apoptosis. It is toxic to insulin-producing cells and commonly used to establish diabetic animal models. This product is unstable in solution and is recommended to be prepared freshly before use. |
| Targets&IC50 | DNA methylating (C1498 cells):1024 μg/mL, DNA methylating (K562 cells):904 μg/mL, DNA methylating (HL6 cells cells):11.7 μg/mL |
| In vitro | METHODS: Rat β-insulinoma cells Rin-5F were treated with Streptozocin (1-10 mM) for 2-48 h. Cell viability was measured using MTT assay. RESULTS: Maximum inhibition (60-70%) was observed in cells treated with 10 mM Streptozocin for 24 h and 48 h. The cells were treated with Streptozocin (1-10 mM) for 2-48 h, and cell viability was measured by MTT assay. [1] METHODS: Neural stem cells were treated with Streptozocin (2.5 mM) for 2 days and gene expression was detected using RT-qPCR. RESULTS: Streptozocin significantly reduced the relative expression level of GLUT3 mRNA by 46.4%, and did not affect the relative expression level of IR and GLUT1. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: Streptozocin (40 mg/kg in the 50 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 4.5), ready to use) was administered intraperitoneally to C57BL/6 or CD-1 male mice once daily for five days. Normal food and 10% sucrose water were provided during the administration period, and 10% sucrose water was replaced with normal water on the sixth day. RESULTS: Repeated low doses of Streptozocin induced type 1 diabetes in mice. [3] METHODS: Streptozocin (200 mg/kg in the 50 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 4.5), ready to use) was administered to C57BL/6 or CD-1 male mice by a single intraperitoneal injection. Normal food and 10% sucrose water were provided after administration, and 10% sucrose water was replaced with normal water on the third day. RESULTS: A single high dose of Streptozocin induced type 1 diabetes in mice. [3] |
| Cell Research | Streptozocin (STZ) stock solutions of 50 mg/mL in distilled Water (dWater) are freshly prepared for each experiment[2]. Human and murine cell lines are cultured in triplicate in 96-well plates at a density of 2×104 cells/well in the absence (untreated control) or presence of various concentrations of ALX (20-3000 μg/mL) or STZ (1-3000 μg/mL) for 48 h at 37°C under a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Cells incubated in complete media including dWater in a final concentration of 0.1% served as control for solvent toxicity and cells incubated in complete medium are used as a control for the experiments. The effects of the tested drugs on tumor cell growth or viability are determined employing the MTT assay in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. The IC50values (drug concentration that induces 50% inhibition of the cell growth) are calculated using the GraphPad Prism 4 program[2]. |
| Synonyms | U 9889, STZ, Streptozocin, NSC-85998 |
| Molecular Weight | 265.22 |
| Formula | C8H15N3O7 |
| Cas No. | 18883-66-4 |
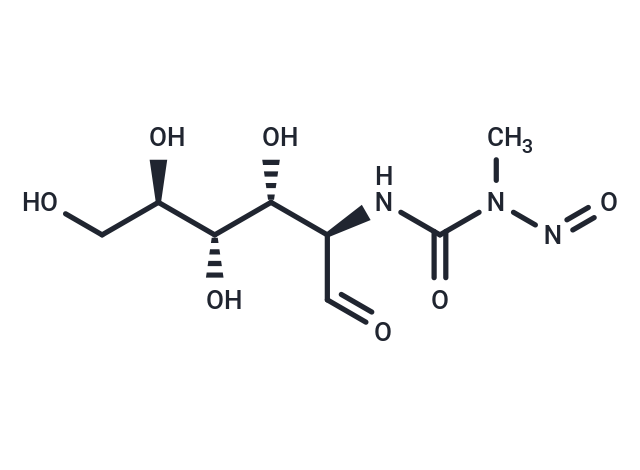
| Smiles | [C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O)O)O)(NC(N(N=O)C)=O)C=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.4410 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature,store under nitrogen,The compound is unstable in solution. Please use soon | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 113.3 mg/mL (427.19 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. DMSO: 16.67 mg/mL (62.85 mM), Sonication is recommended.(The compound is unstable in solution, please use soon.) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.