 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Sodium Oxamate (Oxamic acid sodium salt) is an LDH inhibitor that specifically inhibits LDHA. Sodium Oxamate has antitumor activity and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $31 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in H2O) | $39 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Sodium Oxamate (Oxamic acid sodium salt) is an LDH inhibitor that specifically inhibits LDHA. Sodium Oxamate has antitumor activity and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. |
| Targets&IC50 | A549 cells:19.67 ± 1.53 mM, H1299 cells:32.13 ± 2.50 mM, HBE:96.73 ± 7.60 mM, MIAPaCa2 cells:18.9 mM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human lung cancer cells H1299, A549 and normal human bronchial epithelial cells HBE were treated with Sodium Oxamate (1-100 mmol/L) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK-8 assay. RESULTS: Sodium Oxamate significantly inhibited the cell viability of H1299 and A549 cells in a dose-dependent manner, with IC50 of 32.13±2.50 and 19.67±1.53 mmol/L, respectively. Sodium Oxamate had almost no effect on HBE cells, with an IC50 of 96.73±7.60 mmol/L. [1]. METHODS: Human lung cancer cells A549 and normal human bronchial epithelial cells HBE were treated with Sodium Oxamate (20-100 mmol/L) for 24 h, and several intracellular biochemical parameters were measured. RESULTS: LDH activity, ATP content and NADPH/NADP ratio were significantly decreased and ROS content was significantly increased in A549 cells after Sodium Oxamate treatment. In contrast, glucose metabolism was less affected, although LDH enzyme was also inhibited in a dose-dependent manner in HBE cells. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To detect the antitumor activity in vivo, Sodium Oxamate (300 mg/kg once a day) and pembrolizumab (10 mg/kg twice a week) were intraperitoneally injected into B-NDG mice carrying human lung cancer tumor H1299 for fifteen days. RESULTS: Both Sodium Oxamate and pembrolizumab significantly delayed tumor growth in monotherapy, and the combination therapy was more effective. [1] METHODS: To explore the potential for the treatment of diabetes, Sodium Oxamate (350-750 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to db/db mice once daily for twelve weeks. RESULTS: Sodium Oxamate treatment reduced body weight gain, blood glucose and HbA1c levels, and improved insulin secretion, pancreatic islet morphology, and insulin sensitivity in db/db mice.Sodium Oxamate improves glycemic control and insulin sensitivity in db/db mice, primarily by inhibiting the production of tissue lactic acid. [3] |
| Synonyms | SO, Oxamic acid sodium salt, oxamate sodium, Aminooxoacetic acid sodium salt |
| Molecular Weight | 111.03 |
| Formula | C2H2NNaO3 |
| Cas No. | 565-73-1 |
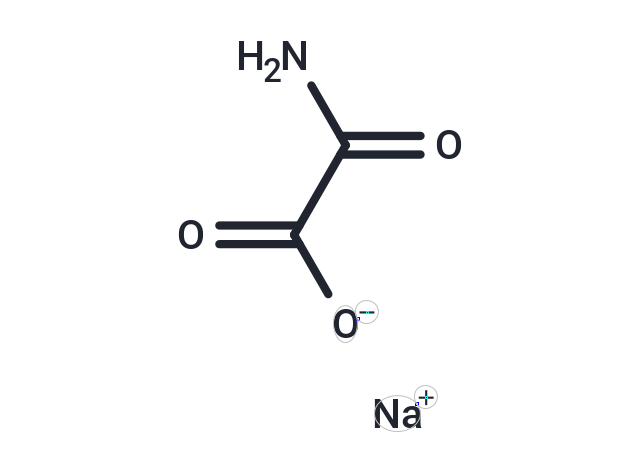
| Smiles | [Na+].NC(=O)C([O-])=O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | store under nitrogen | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 25.5 mg/mL (229.67 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: Insoluble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.