Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

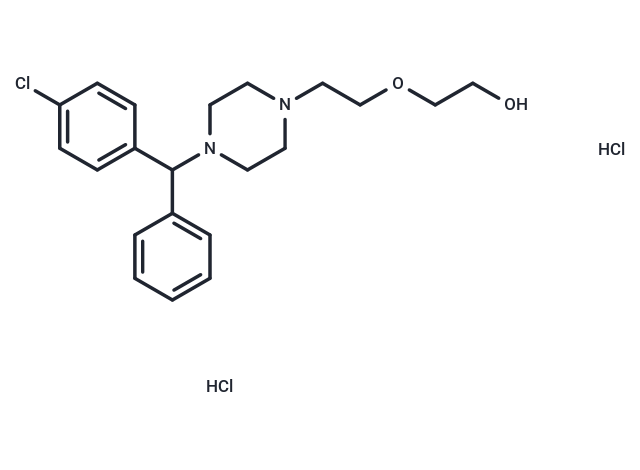
Hydroxyzine dihydrochloride (Hydroxyzine 2HCl) is a histamine H1 receptor antagonist that is effective in the treatment of chronic urticaria, dermatitis, and histamine-mediated pruritus. Unlike its major metabolite CETIRIZINE, it does cause drowsiness. It is also effective as an antiemetic, for relief of anxiety and tension, and as a sedative.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $29 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $35 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $48 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock |
| Description | Hydroxyzine dihydrochloride (Hydroxyzine 2HCl) is a histamine H1 receptor antagonist that is effective in the treatment of chronic urticaria, dermatitis, and histamine-mediated pruritus. Unlike its major metabolite CETIRIZINE, it does cause drowsiness. It is also effective as an antiemetic, for relief of anxiety and tension, and as a sedative. |
| Targets&IC50 | H1 receptor:10 nM-19 nM |
| In vitro | In a tail-flick test, intraperitoneal injection of 12.5 mg/kg Hydroxyzine reduced the analgesic effect of morphine in rats; however, an injection of 50 mg/kg Hydroxyzine enhanced the effect of morphine. Furthermore, 500 μM Hydroxyzine significantly decreased the steady-state concentration of etoposide by half, achieving a concentration of 0.055 μM/mL in Sprague-Dawley rats. |
| In vivo | At a concentration of 0.1 mM, Hydroxyzine inhibits 50% of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) exacerbation in Lewis rats and suppresses 70% of mast cell degranulation. In bladder slices pre-treated with Hydroxyzine, a 60-minute incubation results in a 34% inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine release induced by 10 μM carbachol, with 1 μM Hydroxyzine causing a 25% inhibition and 0.1 μM suppressing it by 17%. Additionally, 500 μM Hydroxyzine significantly enhances the transport of digoxin to the serosal side in isolated everted jejunum sacs and notably reduces the efflux of approximately 2.4 μg/mL digoxin in the jejunum and ileum. |
| Alias | Hydroxyzine 2HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 447.83 |
| Formula | C21H27ClN2O2·2HCl |
| Cas No. | 2192-20-3 |
| Smiles | C1CN(CCN1CCOCCO)C(c1ccccc1)c1ccc(cc1)Cl.Cl.Cl |
| Relative Density. | 1.182 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 201 mM, Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 55 mg/mL (122.81 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.