Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Esculetin (Cichorigenin) is a coumarin derivative from various natural plant products with various biological and pharmaceutical properties including anti-edema, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumour effects. It inhibits lipoxygenases (LOs).
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $45 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Esculetin (Cichorigenin) is a coumarin derivative from various natural plant products with various biological and pharmaceutical properties including anti-edema, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumour effects. It inhibits lipoxygenases (LOs). |
| In vitro | Esculetin decreases cell proliferation by inducing G1 phase cell cycle arrest, which is associated with the down-regulation of cyclin D1/CDK4 and cyclin E/CDK2 complexes by the activation of p27KIP[2]. Esculetin significantly inhibits proliferation of HCC cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner and with an IC50 value of 2.24 mM. It blocks the cell cycle at S phase and induces apoptosis in SMMC-7721 cells with significant elevation of caspase-3 and caspase-9 activity, but does not affect caspase-8 activity. Esculetin treatment results in the collapse of mitochondrial membrane potential in vitro and in vivo accompanied by increased Bax expression and decreased Bcl-2 expression at both transcriptional and translational levels. Esculetin exerts in vitro and in vivo antiproliferative activity in hepatocellular carcinoma, and its mechanisms involved initiation of a mitochondrial-mediated, caspase-dependent apoptosis pathway[3]. |
| In vivo | Esculetin significantly decreases tumor growth in mice bearing Hepa1-6 cells. Tumor weight is decreased by 20.33, 40.37, and 55.42% with increasing doses of esculetin. Of note, esculetin has no obvious toxicity in this animal study[3]. In a rat experimental model of inflammatory bowel disease induced by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid, esculetin at the dose of 5 mg/kg displays intestinal anti-inflammatory activity[4]. |
| Cell Research | Tests are performed in 96-well plates. For mature adipocytes, cells are seeded (5000 cells/well), grown to confluency, induced to differentiate, and grown to maturation. For preadipocytes, a seeding density of 2500 cells/well is used, and cells are cultured overnight before treatment. Cells are incubated with either DMSO or increasing concentrations of esculetin for 6, 12, 24, or 48 hours. For the post-confluent preadipocytes, a seeding density of 2500 cells/well is used, and cells are grown to confluency before treatment. Esculetin (100 or 200 μM) in 0.01% DMSO carrier is added with the induction medium for Days 0 to 2, 2 to 4, and 4 to 6 of adipogenesis. Medium is changed every 2 days. Before assay for cell viability, cells are washed with DMEM/10% FBS three times, and 100 μL of DMEM/10% FBS medium is added to each well before treatment with 20 μL MTS assay solution per well. Cells are incubated for 1 hour at 37 °C; then 25 μL of 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate is added to each well. The absorbance is measured at 490 nm in a plate reader to determine the formazan concentration, which is proportional to the number of live cells.(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | Cichorigenin, Aesculetin |
| Molecular Weight | 178.14 |
| Formula | C9H6O4 |
| Cas No. | 305-01-1 |
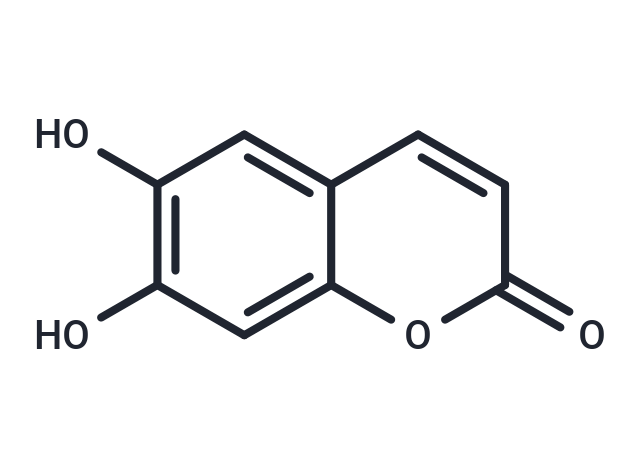
| Smiles | OC1=C(O)C=C2C=CC(=O)OC2=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.563 g/cm3 |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 125 mg/mL (701.7 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (11.23 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.