Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Elsibucol (AGI 1096) is a VCAM1 inhibitor for the study of organ transplant rejection.Elsibucol is a metabolically stable propanol derivative with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative properties. It lowers blood cholesterol levels and reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in injured arteries, thereby inhibiting atherosclerosis and protecting endothelial healing after arterial injury.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $146 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $350 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $530 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $859 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $1,180 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,590 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $3,190 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Elsibucol (AGI 1096) is a VCAM1 inhibitor for the study of organ transplant rejection.Elsibucol is a metabolically stable propanol derivative with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative properties. It lowers blood cholesterol levels and reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in injured arteries, thereby inhibiting atherosclerosis and protecting endothelial healing after arterial injury. |
| In vitro | Elsibucol(0-20 μM) inhibited the inducible expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1, E-selectin, and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 in endothelial cells and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and interleukin (IL)-1beta secretion from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. It also inhibited the serum-stimulated proliferation of aortic smooth muscle cells.[4] |
| In vivo | Elsibucol (0.5%, 1%; feed; arterial injury in rabbits with hypercholesterolemia; 3 weeks) significantly decreases blood total cholesterol, LDLc, and triglyceride levels. This is associated with a significant 46% reduction of neointimal hyperplasia following arterial injury. Interestingly, the effect of Elsibucol on cholesterol levels and neointimal formation appears to be more pronounced than that of probucol. Treatment with Elsibucol is associated with a significant reduction of cellular proliferation (PCNA immunostaining), oxidative stress (nitrotyrosine immunostaining), VCAM-1 expression, and macrophage infiltration in injured arteries. Despite its potent effect on neointimal hyperplasia, Elsibucol does not prevent endothelial healing (Evans blue staining) following arterial injury. CONCLUSIONS: In hypercholesterolemic animals, Elsibucol inhibits atherosclerosis and preserves endothelial healing following arterial injury.[1] |
| Synonyms | UNII-O7T92N1Y8T, AGI-1096, AGI 1096 |
| Molecular Weight | 602.93 |
| Formula | C35H54O4S2 |
| Cas No. | 216167-95-2 |
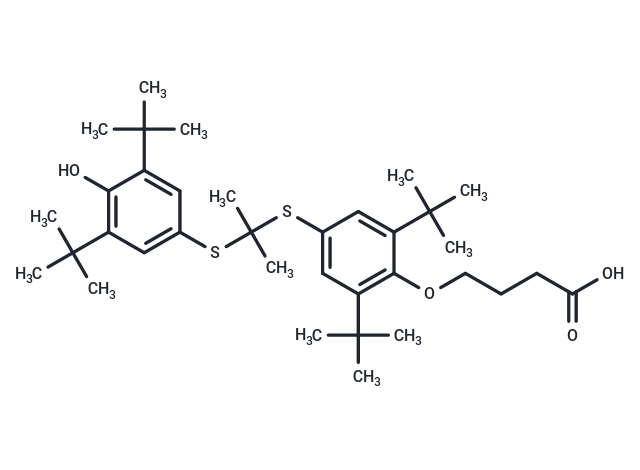
| Smiles | O(CCCC(O)=O)C1=C(C(C)(C)C)C=C(SC(SC2=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C2)(C)C)C=C1C(C)(C)C |
| Relative Density. | 1.10 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (82.93 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+90% Corn Oil: 2.5 mg/mL (4.15 mM), Sonication is recommeded. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.