 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Cardioxane (ADR-529) is a cardio-protective drug.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $46 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $68 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $92 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $121 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $317 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $32 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Cardioxane (ADR-529) is a cardio-protective drug. |
| In vitro | Dexrazoxane (10 mM), known clinically to limit anthracycline cardiac toxicity, prevents daunorubicin-induced myocyte apoptosis, but not necrosis induced by higher anthracycline concentrations in rat cardiac myocytes. [1] Dexrazoxane presumably exerts its cardioprotective effects by either binding free or loosely bound iron, or iron complexed to doxorubicin, thus preventing or reducing site-specific oxygen radical production that damages cellular components. [2] Dexrazoxane specifically abolishes the DNA damage signal gamma-H2AX induced by doxorubicin, but not camptothecin or hydrogen peroxide, in H9C2 cardiomyocytes. Dexrazoxane also induces rapid degradation of Top2beta, which paralleles the reduction of doxorubicin-induced DNA damage. Dexrazoxane antagonizes doxorubicin-induced DNA damage through its interference with Top2beta, which could implicate Top2beta in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. [3] Dexrazoxane is hydrolyzed to its active form intracellularly and binds iron to prevent the formation of superhydroxide radicals, thus preventing mitochondrial destruction. [4] |
| In vivo | Dexrazoxane combined with doxorubicin, daunorubicin, or idarubicin reduces the tissue lesions in B6D2F1 mice (expressed as area under the curve of wound size times duration) by 96%, 70%, and 87%, respectively. Dexrazoxane combined with doxorubicin, daunorubicin, or idarubicin results in a statistically significant reduction in the fraction of mice with wounds as well as the duration of wounds. [5] |
| Kinase Assay | HTRF assay: Homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) assay measures the signal generated by 2 components when they are in close proximity. The p53–MDM2 binding assay uses a biotinylated peptide derived from the MDM2-binding domain of p53 and a truncated N-terminal portion of recombinant human GST-tagged MDM2 protein containing the p53-binding domain. Proteins for crystal structure studies are expressed in E. coli strain BL21 using the helper plasmid pUBS 520 coding for the lacIq repressor and the rare tRNAArg [AGA/AGG]. For crystallization, the frozen protein is thawed and concentrated to 9.8 mg/mL using a Centricon concentrator (3,000 MW cutoff). The complex is then formed by combining the protein with a slight molar excess of the inhibitor (stock solution is 100 mM in DMSO) and this solution is allowed to sit for 4 hours at 4°C. Cryopreserved crystals are used to collect diffraction data on beamline X8C at the National Synchrotron Light Source at Brookhaven National Laboratory. |
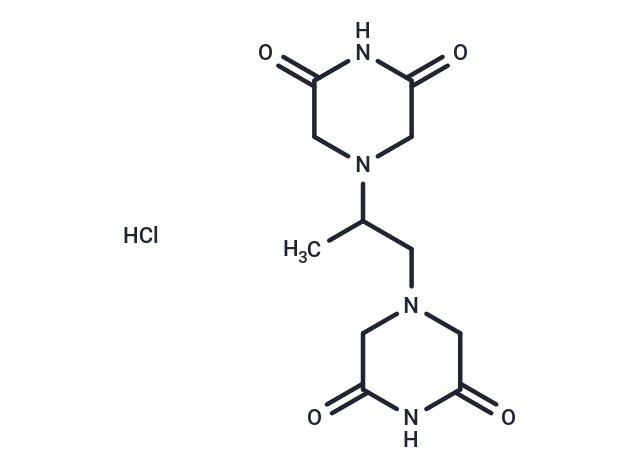
| Synonyms | ICRF-187 hydrochloride, ICRF-187, Dexrazoxane HCl, Cardioxane hydrochloride, ADR-529 Hydrochloride, ADR-529 |
| Molecular Weight | 304.73 |
| Formula | C11H16N4O4·HCl |
| Cas No. | 149003-01-0 |
| Smiles | Cl.CC(CN1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1)N1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 55 mg/mL (180.49 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (164.08 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (8.2 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.