Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

CCF642 (AC1LYELL) is a novel PDI-inhibiting compound with antimyeloma activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $64 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $94 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $198 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $329 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $492 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $718 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $64 | In Stock |
| Description | CCF642 (AC1LYELL) is a novel PDI-inhibiting compound with antimyeloma activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | PDI:2.9 μmol/L |
| In vitro | In vitro, CCF642 inhibits PDI reductase activity about 100-fold more potently than the structurally distinct established inhibitors PACMA 31 and LOC14. Computational modeling suggests a novel covalent binding mode in active-site CGHCK motifs. CCF642 causes acute ER stress in multiple myeloma cells accompanied by apoptosis-inducing calcium release[1]. |
| In vivo | CCF642 displays potent efficacy in an aggressive syngeneic mouse model of multiple myeloma and prolongs the lifespan of C57BL/KaLwRij mice engrafted with 5TGM1-luc myeloma, an effect comparable to the first-line multiple myeloma therapeutic bortezomib[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Inhibition of CB-839 on rHu-GAC: The enzymatic activity is measured in assay buffer containing 50 mM Tris-Acetate pH 8.6, 150 mM K2HPO4 , 0.25 mM EDTA, 0.1 mg/mL bovine serum albumin, 1 mM DTT, 2 mM NADP+ and 0.01% Triton X-100. To measure inhibition, the inhibitor (prepared in DMSO) is first pre-mixed with glutamine and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) and reactions are initiated by the addition of rHu-GAC. Final reactions contains 2 nM rHu-GAC, 10 mM glutamine, 6 units/mL GDH and 2% DMSO. Generation of NADPH is monitored by fluorescence (Ex340/Em460 nm) every minute for 15 minutes on a SpectraMax M5e plate reader. Relative fluorescence units (RFU) are converted to units of NADPH concentration (μM) using a standard curve of NADPH. Each assay plate incorporates control reactions that monitores the conversion of glutamate (1 to 75 μM) plus NADP+ to α-ketoglutarate plus NADPH by GDH. Under these assay conditions, up to 75 μM glutamate is stoichiometrically converts to α-ketoglutarate/NADPH by GDH. Initial reaction velocities are calculated by fitting the first 5 minutes of each progress curve to a straight line. Inhibition curves are fitted to a four-parameter dose response equation of the form: % activity = Bottom + (Top-Bottom)/(1+10^((LogIC50-X)*HillSlope)). |
| Alias | AC1LYELL |
| Molecular Weight | 378.45 |
| Formula | C15H10N2O4S3 |
| Cas No. | 346640-08-2 |
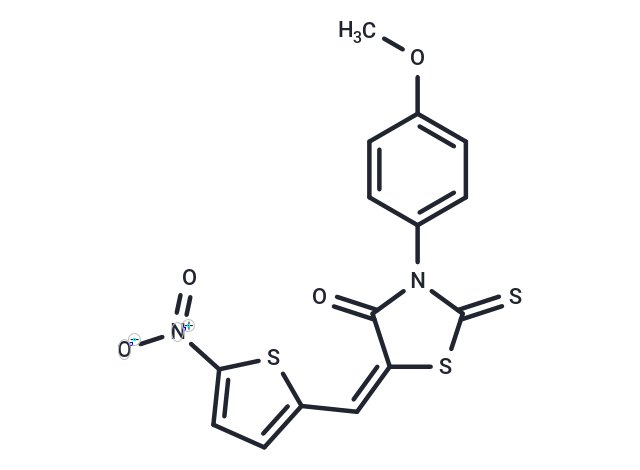
| Smiles | COc1ccc(cc1)N1C(=S)S\C(=C\c2ccc(s2)[N+]([O-])=O)C1=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.60 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 11.11 mg/mL (29.36 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.