 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

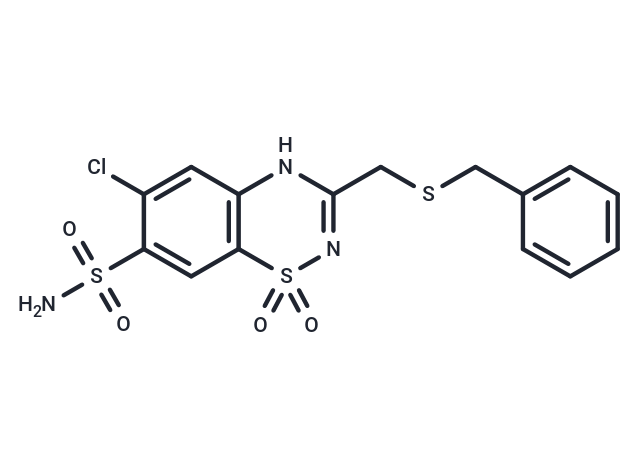
Benzthiazide (Lemazide) is used in the therapy of edema and hypertension. Like other thiazides, benzthiazide accelerates water loss from the body (diuretics). They inhibit Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys. Thiazides also cause loss of potassium and an increase in serum uric acid. Thiazides are often used to treat hypertension, but their hypotensive effects are not necessarily due to their diuretic activity. Thiazides have been shown to prevent hypertension-related morbidity and mortality although the mechanism is not fully understood. Thiazides cause vasodilation by activating calcium-activated potassium channels (large conductance) in vascular smooth muscles and inhibiting various carbonic anhydrases in vascular tissue.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $39 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $43 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Benzthiazide (Lemazide) is used in the therapy of edema and hypertension. Like other thiazides, benzthiazide accelerates water loss from the body (diuretics). They inhibit Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys. Thiazides also cause loss of potassium and an increase in serum uric acid. Thiazides are often used to treat hypertension, but their hypotensive effects are not necessarily due to their diuretic activity. Thiazides have been shown to prevent hypertension-related morbidity and mortality although the mechanism is not fully understood. Thiazides cause vasodilation by activating calcium-activated potassium channels (large conductance) in vascular smooth muscles and inhibiting various carbonic anhydrases in vascular tissue. |
| Targets&IC50 | Carbonic anhydrase II:8.8 nM (Ki), CA9:8.0 nM (Ki), Carbonic anhydrase I:10 nM (Ki) |
| Synonyms | Lemazide, Dihydrex, Aquatag |
| Molecular Weight | 431.94 |
| Formula | C15H14ClN3O4S3 |
| Cas No. | 91-33-8 |
| Smiles | NS(=O)(=O)c1cc2c(NC(CSCc3ccccc3)=NS2(=O)=O)cc1Cl |
| Relative Density. | 1.4176 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (115.76 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (4.63 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.