 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

BAPTA-AM is a calcium chelator that is cell-permeable and selective, blocking hERG, hKv1.3, and hKv1.5 channels (IC50=1.3/1.45/1.23 μM). BAPTA-AM has a 105-fold higher affinity for Ca2+ than for Mg2+, and can be used for the role of calcium in cell signaling.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $51 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | Preferential | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | Preferential | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $43 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | BAPTA-AM is a calcium chelator that is cell-permeable and selective, blocking hERG, hKv1.3, and hKv1.5 channels (IC50=1.3/1.45/1.23 μM). BAPTA-AM has a 105-fold higher affinity for Ca2+ than for Mg2+, and can be used for the role of calcium in cell signaling. |
| Targets&IC50 | Kv1.3 channel (human, HEK293 cells):1.45 μM, Kv1.5 channel (human, HEK293 cells):1.23 μM, ERG channel (human, HEK293 cells):1.3 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Chondrocytes were treated with BAPTA-AM (10 μM) and FAC (100 μM) for 24 h. Intracellular ROS levels were measured using the Reactive Oxygen Species Assay kit. RESULTS: FAC promoted ROS production and this effect was inhibited by the calcium chelator BAPTA-AM. [1] METHODS: Rat fibroblast RAT2 and Xenopus cells were treated with BAPTA-AM (50 μM) for 1 h, and microtubule depolymerization was detected by Immunostaining. RESULTS: BAPTA AM treatment for 30 min resulted in almost complete disassembly in most cells, and microtubules were uniformly depolymerized in cells within 60 min. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To investigate the effect on ethanol-induced locomotor activity, BAPTA-AM (0-10 mg/kg, Cremophor EL 1.25% (v/v) in distilled water) was injected intraperitoneally into Swiss (RjOrl) mice, followed by ethanol (0-4 g/kg) 30 min later. RESULTS: Pretreatment with BAPTA-AM blocked the locomotor stimulus produced by ethanol without altering basal locomotion. On the contrary, BAPTA-AM reversed the ethanol-induced hypnosis. [3] METHODS: To investigate the effect on LPS-induced blood-brain barrier leakage, BAPTA-AM (12 mg/kg, 0.01% pluronic acid in sterile saline) was injected intravenously into FVB mice, followed 30 min later by intraperitoneal injection of LPS (25 mg/kg). RESULTS: BAPTA-AM reduced LPS-induced blood-brain barrier leakage. [4] |
| Cell Research | Instructions for use I. Solution preparation 1. Prepare BAPTA-AM storage solution: Dissolve BAPTA-AM in anhydrous DMSO to prepare a 50 mM storage solution; (it is recommended to store at -20 ℃ or -80 ℃ in the dark after aliquoting). 2. Prepare working solution: Dilute BAPTA-AM storage solution into cell culture medium to a final concentration of 6-50 μM. II. Cell preparation 1. Grow cells to an appropriate density. For adherent cells, they can be planted in culture dishes or culture plates; for suspended cells, adjust the cell concentration to 2×10^6 cells/mL. 2. Incubate cells with BAPTA-AM solution, usually at 37℃, 5% CO₂ for 30-60 minutes, with gentle shaking during the period. 3. Remove excess dye: After incubation, wash cells with calcium-free buffer to remove BAPTA-AM that has not entered the cells. 4. For adherent cells, they can be directly washed with calcium-free PBS; for suspended cells, the cells need to be collected by centrifugation and then resuspended with calcium-free PBS. 5. Detection of changes in calcium ion concentration: You can choose the appropriate detection method according to the experimental requirements: Fluorescence microscope detection: observe the changes in fluorescence intensity in cells. The decrease in fluorescence intensity indicates a decrease in calcium ion concentration. Flow cytometry detection: analyze the changes in fluorescence intensity in cells through flow cytometry. Fluorescence spectrometer detection: measure the changes in fluorescence intensity of cell suspension. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Synonyms | BAPTA/AM |
| Molecular Weight | 764.68 |
| Formula | C34H40N2O18 |
| Cas No. | 126150-97-8 |
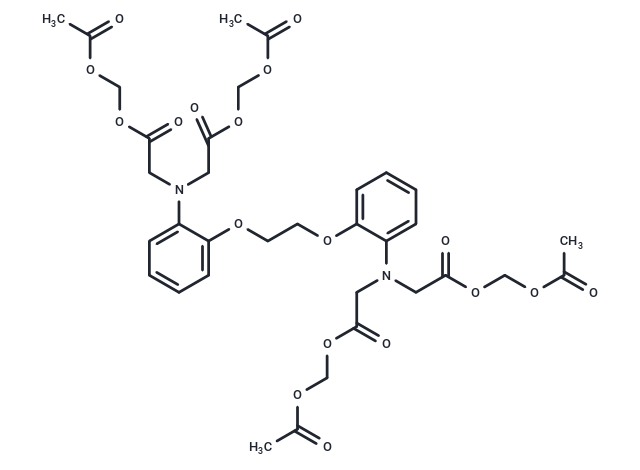
| Smiles | CC(=O)OCOC(=O)CN(CC(=O)OCOC(C)=O)c1ccccc1OCCOc1ccccc1N(CC(=O)OCOC(C)=O)CC(=O)OCOC(C)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.35 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (130.77 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (3.27 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.