Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
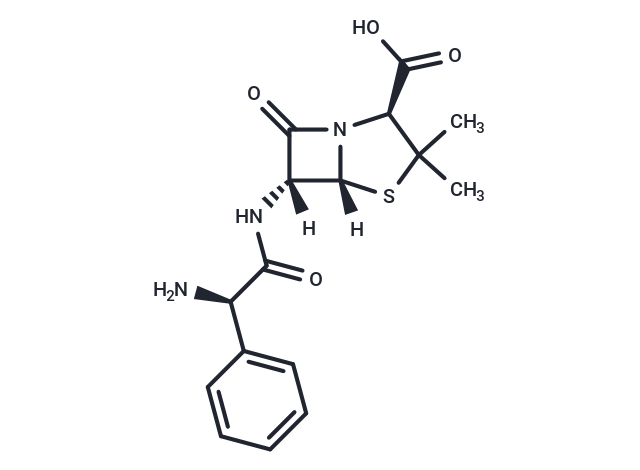
Ampicillin (Aminobenzylpenicillin) is a semi-synthetic penicillin belonging to the β-lactam group of antibiotics. Ampicillin has bactericidal activity against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $30 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Ampicillin (Aminobenzylpenicillin) is a semi-synthetic penicillin belonging to the β-lactam group of antibiotics. Ampicillin has bactericidal activity against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. |
| Targets&IC50 | transporter:9.9 mM (Ki), carnitine/carnitine antiport:7.6 mM, enzyme transpeptidase:1.8 µg/mL, HEK293 cells:> 100 μM (CC50) |
| In vitro | METHODS: E. coli was treated with Ampicillin (0.1-10 μG/mL) for 6 h. Growth was measured using a Fisher Electrophotometer. RESULTS: No differences in E. coli growth were observed at concentrations of 0, 0.1, and 1.0 μG. 2.5, 5, and 10 μG concentrations of Ampicillin inhibited E. coli growth. [1] METHODS: Pharyngeal cancer cells Detroit-562 were treated with Ampicillin (10-100 μM) for 72 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT. RESULTS: The Ampicillin-treated groups at concentrations of 10, 25 and 50 μM showed higher cell viability than the control cells, with values of 112%, 107% and 106%, respectively. At concentrations of 75 and 100 μM, there was a slight but not significant decrease in cell viability with values of approximately 95% and 94%, respectively. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To test the neuroprotective mechanism in a mouse model of transient total forebrain ischemia, Ampicillin (200 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally into C57BL/6 mice once a day for five days, and forebrain ischemia was induced 24 h after the last injection. RESULTS: Pretreatment with Ampicillin significantly attenuated neuronal damage in the CA1 subregion of the hippocampus, and Ampicillin may provide neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inducing GLT-1 protein and inhibiting MMP activity in the hippocampus of mice. [3] METHODS: To study the in vivo activity, Ampicillin (10-100 mg/kg) was administered by gavage to C57BL/6 mice once daily for two days. RESULTS: Exposure of mice to Ampicillin induced anxiety and colitis, and increased Aspergillus flora in the gut microbiota. [4] |
| Synonyms | D-(-)-α-Aminobenzylpenicillin, Ampicillin acid, Aminobenzylpenicillin, Amcill |
| Molecular Weight | 349.4 |
| Formula | C16H19N3O4S |
| Cas No. | 69-53-4 |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(NC(=O)[C@H](N)c2ccccc2)C(=O)N2[C@@H](C(O)=O)C(C)(C)S[C@]12[H] |
| Relative Density. | 1.2794 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 240 mg/mL (686.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. 0.1 M NaOH: 25 mg/mL (71.55 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.1 M NaOH/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.