 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Amonafide (NSC-308847,AS1413)(AS1413) produces protein-associated DNA-strand breaks through a topoisomerase II-mediated reaction, but does not produce topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $33 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $47 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $73 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $89 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $166 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $296 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $491 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $84 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Amonafide (NSC-308847,AS1413)(AS1413) produces protein-associated DNA-strand breaks through a topoisomerase II-mediated reaction, but does not produce topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage. |
| In vitro | Through a topoisomerase II-mediated reaction, Amonafide treatment produces DNA single-strand breaks (SSB), double-strand breaks (DSB), and DNA-protein cross-links in human myeloid leukemia cells. Amonafide treatment inhibits conlony formation of the leukemic cell lines and the normal human bone marrow GM-CFC in a dose-dependent manner. Amonafide does not produce topoisomerase I-mediated DNA cleavage even at 100 μM. The m-AMSA-resistant line is less than 2-fold resistant to Amonafide [1] Amonafide interferes with the DNA breakage-reunion activity of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II resulting in DNA cleavage stimulation. [2] Compared with those of other antitumor drugs, Amonafide-stimulated cleavage intensity patterns are markedly different. Amonafide highly prefers a cytosine, and excludes guanines and thymines instead, at position -1, with lower preference for an adenine at position +1. [3] Topoisomerase II-mediated DNA cleavage induced by Amonafide is affected only slightly (less than 3-fold) by 1 mM ATP, suggeting that Amonafide is an ATP-insensitive topoisomerase II inhibitor in contrast to doxorubicin, etoposide, and mitoxantrone. [4] Amonafide significantly inhibits the growth of HT-29, HeLa, and PC3 cells with IC50 of 4.67 μM, 2.73 μM, and 6.38 μM, respectively. [5] Amonafide is unaffected by P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux, unlike those of the classical topoisomerase II inhibitors (daunorubicin, doxorubicin, idarubicin, etoposide, and mitoxantrone). [6] |
| Cell Research | All cell lines are in the logarithmic phase of growth when the assay of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) is carried out. Cells are harvested and seeded into 96-well tissue culture plates at a density of 2.5 × 103 cells/well in 150 μL aliquots of medium. The concentrations tested are serial dilutions of a stock solution (10 μM in DMSO) with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and are added 24 hours later. The assay is ended after 72 hours of Amonafide exposure and PBS is used as a negative control. After 72 hours treatment, cells are washed twice with PBS, and then 50 μL/well of MTT reagent (1 mg/mL in PBS) together with 150 μL/well of prewarmed medium are added. The plates are returned to the incubator for 4 hours. Subsequently, DMSO is added as solvent. Absorbance is determined at 570 nm with a Microplate reader. All experiments are performed at least three times, and the average of the percentage absorbance is plotted against concentration. Then, the concentration of Amonafide required to inhibit 50% of cell growth (IC50) is calculated for Amonafide.(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | Quinamed, NSC308847, Nafidimide, AS1413 |
| Molecular Weight | 283.33 |
| Formula | C16H17N3O2 |
| Cas No. | 69408-81-7 |
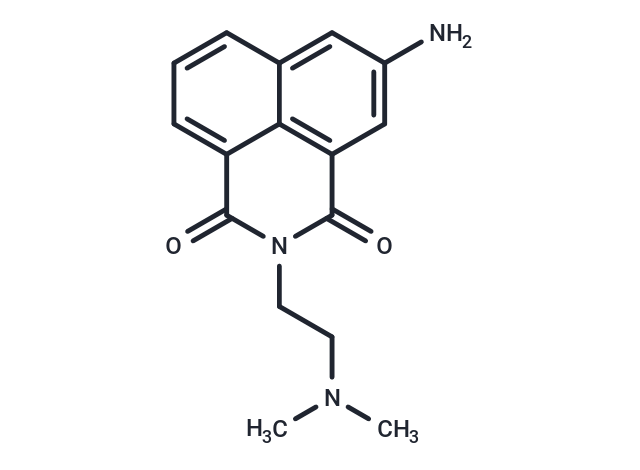
| Smiles | CN(C)CCN1C(=O)c2cccc3cc(N)cc(C1=O)c23 |
| Relative Density. | 1.306 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 53 mg/mL (187.06 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 4 mg/mL (14.12 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (7.06 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.