 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

8-Aminoadenosine (8-NH2-Ado) is an RNA-directed nucleoside analogue that effectively diminishes cellular ATP levels and impedes mRNA synthesis. It also obstructs Akt/mTOR signaling, inducing autophagy and apoptosis in a p53-independent manner. Its significant antitumor activity underscores its therapeutic potential.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $62 | 5 days | 5 days |
| Description | 8-Aminoadenosine (8-NH2-Ado) is an RNA-directed nucleoside analogue that effectively diminishes cellular ATP levels and impedes mRNA synthesis. It also obstructs Akt/mTOR signaling, inducing autophagy and apoptosis in a p53-independent manner. Its significant antitumor activity underscores its therapeutic potential. |
| In vitro | 8-Aminoadenosine (8-NH2-Ado) demonstrates a range of bioactive effects across various cell lines. In MM.1S and U266 cells, it exhibits half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) of 1.5 μM and 8.88 μM, respectively, after a 48-hour exposure[1]. At a concentration of 10 μM over 24 hours, it induces significant apoptotic death of MCF-7 cells through a p53-independent mechanism, characterized by PARP cleavage[2]. Additionally, at a concentration of 3 μM, 8-Aminoadenosine triggers autophagy in MM.1S cells within 0.5 to 4 hours, and notably reduces ATP levels and glucose consumption over similar durations[1]. This compound also causes a marked time-dependent decrease in GLUT1 expression initially, with subsequent down-regulation of both GLUT1 and GLUT4 transporters over a longer period (24 hours)[1]. It is observed to inhibit cell proliferation and induce cell death without activating p53 pathway targets or increasing p53 or p21 proteins. Its toxicological actions are adenosine kinase activity-dependent, requiring conversion to 8-NH2-ATP in specifically adenosine kinase-deficient cells[1]. Analysis of cell viability and apoptosis under various concentrations and timeframes further corroborates its impact on cell survival and apoptotic pathways[1][2]. |
| Synonyms | 8-NH2-Ado |
| Molecular Weight | 282.26 |
| Formula | C10H14N6O4 |
| Cas No. | 3868-33-5 |
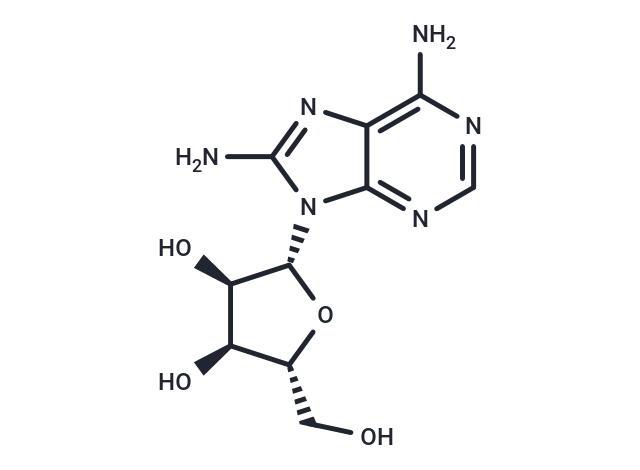
| Smiles | NC=1N(C=2C(N1)=C(N)N=CN2)[C@@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]3O |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.