 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

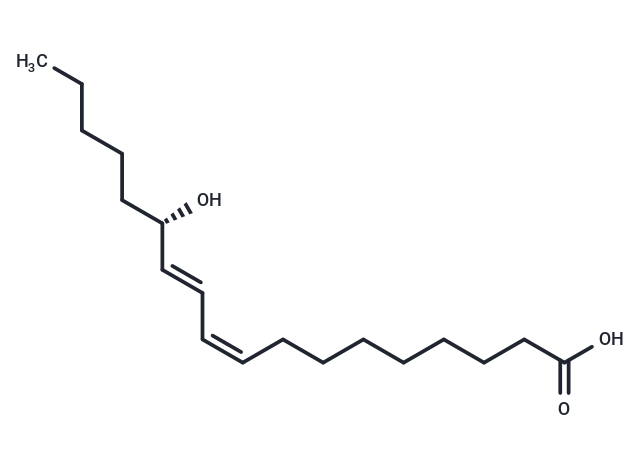
(S)-Coriolic acid (13(S)-HODE) is an important intracellular signaling agent generated by the reaction of linoleic acid with plant and mammalian lipoxygenases. It is involved in cell proliferation and differentiation in various biological systems and inhibits the adhesion of tumor cells to the vascular endothelium, while down-regulating IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor expression at around 1 μM. Additionally, (S)-Coriolic acid is a metabolite of 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX) and often acts as an endogenous ligand to activate PPARγ. It induces mitochondrial dysfunction and airway epithelial damage.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 ug (337.33 μM* 1 mL in Ethanol) | $389 | - | In Stock | |
| 250 ug (337.33 μM * 2.5 mL in Ethanol) | $780 | - | In Stock | |
| 500 ug (337.33 μM * 5 mL in Ethanol) | $1,450 | - | In Stock |
| Description | (S)-Coriolic acid (13(S)-HODE) is an important intracellular signaling agent generated by the reaction of linoleic acid with plant and mammalian lipoxygenases. It is involved in cell proliferation and differentiation in various biological systems and inhibits the adhesion of tumor cells to the vascular endothelium, while down-regulating IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor expression at around 1 μM. Additionally, (S)-Coriolic acid is a metabolite of 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX) and often acts as an endogenous ligand to activate PPARγ. It induces mitochondrial dysfunction and airway epithelial damage. |
| In vitro | (S)-Coriolic acid (30 nM; 6 h; E-FABP-/- keratinocytes) induces K1 expression through NF-κB activation. (S)-Coriolic acid also increases the phosphorylation of Ikkinase-bat tyrosine 199, which promotes IκBα phosphorylation and subsequent NF-kB activation. (S)-Coriolic acid increases the phosphorylation of IκBαat serine 32, which induces IκB degradation and thereby activates NF-κB.[3] |
| In vivo | (S)-Coriolic acid (0-0.6 mg; intranasal; once daily for 3 consecutive days; mouse) induces significant airway dysfunction, neutrophilia, mitochondrial dysfunction, and epithelial injury.[2] |
| Synonyms | 13(S)-HODE |
| Molecular Weight | 296.44 |
| Formula | C18H32O3 |
| Cas No. | 29623-28-7 |
| Smiles | C(=C/C=C\CCCCCCCC(O)=O)\[C@H](CCCCC)O |
| Relative Density. | 0.970 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Pure form: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: >50 mg/mL (per Rao Maddipati), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 55 mg/mL (185.54 mM), Sonication is recommended. PBS (pH 7.2): 1 mg/mL (3.37 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMF: >50 mg/mL (per Rao Maddipati), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PBS (pH 7.2)/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.