 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Etomoxir is an irreversible inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a (CPT-1a) (IC50=5-20 nM). Etomoxir inhibits fatty acid oxidation by inhibiting CPT-1a, inhibits palmitate oxidation, has an inhibitory effect on adenine nucleotide translocase, and can inhibit macrophage polarization by disrupting CoA homeostasis.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $67 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $117 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $197 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $338 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $546 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $74 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Etomoxir is an irreversible inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a (CPT-1a) (IC50=5-20 nM). Etomoxir inhibits fatty acid oxidation by inhibiting CPT-1a, inhibits palmitate oxidation, has an inhibitory effect on adenine nucleotide translocase, and can inhibit macrophage polarization by disrupting CoA homeostasis. |
| Targets&IC50 | faTT cellsy acid (Hepatocyte cells,human):0.1 μM, faTT cellsy acid (Hepatocyte cells,guinea pig):1 μM, KB cells (human):2.76 μM, faTT cellsy acid (Hepatocyte cells,rat):10 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: A2780/PTX cells were treated with Etomoxir (1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000 nM) and paclitaxel (1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000 nM) for 48 hours, and the growth inhibition of the cells was detected by the CCK-8 method. RESULTS: The IC50 value of Etomoxir decreased from 1589.5 ± 62.5 nM to 817.4 ± 79.7 nM. [1] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the inhibition of cardiac CPT-I activity by Etomoxir, rats were injected with Etomoxir daily for 8 consecutive days at a dose of 20 mg/kg. RESULTS: Rats treated with Etomoxir showed a 44% reduction in cardiac CPT-I activity. METHODS: To study the effects of Etomoxir on blood glucose levels, weight gain, hind limb muscle mass, heart mass and liver mass, Lewis rats were treated with 20 mg/kgEtomoxir for 8 days. RESULTS: Treating Lewis rats with Etomoxir for 8 days did not change the blood glucose level, did not affect general growth characteristics such as weight gain, nor did it affect the muscle mass of the hind limbs. However, both the heart mass and liver mass increased significantly by 11%. [2] |
| Synonyms | (R)-(+)-Etomoxir |
| Molecular Weight | 326.82 |
| Formula | C17H23ClO4 |
| Cas No. | 124083-20-1 |
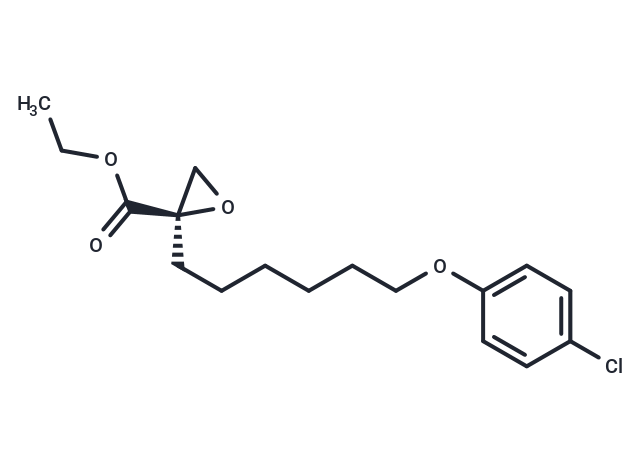
| Smiles | C(OCC)(=O)[C@@]1(CCCCCCOC2=CC=C(Cl)C=C2)CO1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.163 g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature,keep away from moisture | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (764.95 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 0.5% CMC-Na: 12.5 mg/mL (38.25 mM), Suspension. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.