 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

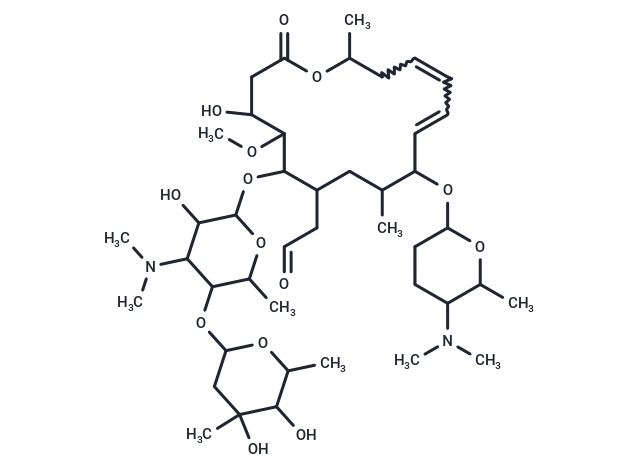
Spiramycin (Rovamycin) is a macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens, effective against gram-positive aerobic pathogens, N. gonorrhoeae, and staphylococci, and is used to treat infections caused by bacteria and Toxoplasma gondii.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $40 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Spiramycin (Rovamycin) is a macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens, effective against gram-positive aerobic pathogens, N. gonorrhoeae, and staphylococci, and is used to treat infections caused by bacteria and Toxoplasma gondii. |
| In vivo | Spiramycin acts by binding to the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit, thereby inhibiting translocation. Its primary mechanism during translocation involves stimulating the dissociation of peptidyl-tRNA from the ribosome. The compound reduces the protective effect of anisomycin on 23S rRNA nucleotides. Spiramycin exhibits potent antibacterial activity against the genus Prevotella, Streptococcus mitis, Archaea, strains of Porphyromonas, and Bacteroides, with metronidazole enhancing its efficacy. At 30°C, Spiramycin can inhibit protein synthesis in wild-type cells but not kill mutant or wild-type cells. Treating lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes with Spiramycin and erythromycin increases the total production of IL-6 without affecting TNFα, IL-1α, or IL-1β production. Spiramycin inhibits protein synthesis by stimulating the dissociation of peptidyl-tRNA from ribosomes. It dose-dependently inhibits the proliferative response of human mononuclear cells stimulated by pulse-width modulation and polyhydroxyalkanoate esters. Additionally, Spiramycin induces a reduction in tritiated thymidine uptake, suggesting interference with an early stage of the cell cycle. |
| Synonyms | Sequamycin, Rovamycin, Provamycin, Formacidine, Espiramicin |
| Molecular Weight | 843.07 |
| Formula | C43H74N2O14 |
| Cas No. | 8025-81-8 |
| Smiles | COC1C(O)CC(=O)OC(C)CC=CC=CC(OC2CCC(C(C)O2)N(C)C)C(C)CC(CC=O)C1OC1OC(C)C(OC2CC(C)(O)C(O)C(C)O2)C(C1O)N(C)C |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 252.5 mg/mL (299.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 93 mg/mL (110.31 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 3.3 mg/mL (3.91 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.