 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

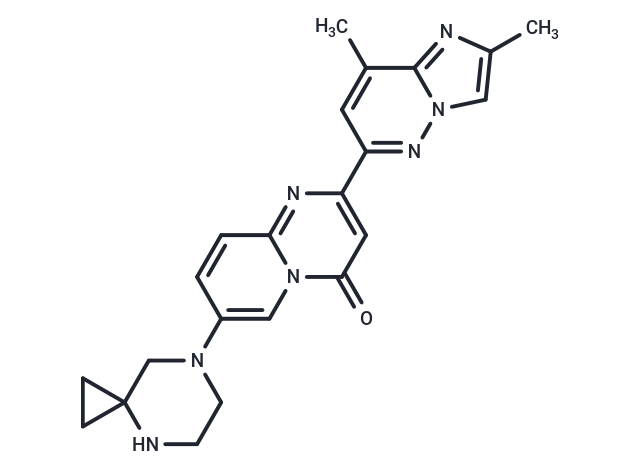
Risdiplam (RG7916) is a centrally and peripherally distributed and orally administrable small molecule SMN2 pre-mRNA splicing modifier that increases survival motor neuron (SMN) protein levels.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $55 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $81 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $129 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $211 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $376 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $559 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $786 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Risdiplam (RG7916) is a centrally and peripherally distributed and orally administrable small molecule SMN2 pre-mRNA splicing modifier that increases survival motor neuron (SMN) protein levels. |
| In vitro | METHODS: LLC-PK1, MDCKII, L-MDR1 (LLC-PK1 cells transfected with human MDR1), L-Mdr1a (LLC-PK1 cells transfected with rodent Mdr1a), M-BCRP (MDCKII cells transfected with human breast cancer resistance protein; BCRP), and M-Bcrp1 (MDCKII cells transfected with rodent Bcrp1) cells were treated with Risdiplam (RG7916) (1 μM) and 10 μM Lucifer Yellow added to the donor compartment to initiate transcellular transport. RESULTS Risdiplam had a mean passive permeability of approximately 350 nm/s in parental LLC-PK1 cells. Similar permeability was observed in L-MDR1, L-Mdra1, M-BCRP, and M-Bcrp cells in the presence of the inhibitor. [1] |
| In vivo | METHODS: Wistar rats received either a single oral dose of 14C-risdiplam (RO7034067) (by gastric gavage) or a single intravenous dose of 14C-risdiplam (by tail vein injection). Dose levels for oral and intravenous doses were 5 or 2 mg/kg, respectively. RESULTS Radioactive 14C-risdiplam (RO7034067) was rapidly and extensively distributed in rat QWBA after oral administration, with peak concentrations in most tissues measured at 2 hours. Radioactivity concentrations in plasma and tissues declined during the study period. [1] |
| Synonyms | RO7034067, RG7916 |
| Molecular Weight | 401.46 |
| Formula | C22H23N7O |
| Cas No. | 1825352-65-5 |
| Smiles | Cc1cn2nc(cc(C)c2n1)-c1cc(=O)n2cc(ccc2n1)N1CCNC2(CC2)C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.50 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 2 mg/mL (4.98 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 2.22 mg/mL (5.53 mM), when pH is adjusted to 6 with HCl. Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.