 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Hesperin (6-MSITC), a flavonoid isolated from orange peel, is a circadian decapping enzyme in plants, inhibiting lipid accumulation and production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in 3T3-L1 and RAW264.7 cells.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg(48.70 mM * 100 μL in Ethanol) | $127 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Hesperin (6-MSITC), a flavonoid isolated from orange peel, is a circadian decapping enzyme in plants, inhibiting lipid accumulation and production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in 3T3-L1 and RAW264.7 cells. |
| In vitro | b>METHODS: HUVEC cells were stimulated with TNF-a or thrombin in the presence of Hesperin (0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1 µg/ml, 4 hours). The effect of Hesperin on VWF release induced by TNF-a and thrombin was studied. RESULTS: Hesperin slightly increased TNF-a-induced TF activity, but at 1 lg/mL (4.88 μM), Hesperin reduced TNF-a- or thrombin-induced TF activity; Hesperin did not change the TF activity of unstimulated HUVECs; indicating that TF activity is inversely proportional to the concentration of Hesperin. [2] |
| In vivo | b>METHODS: Wild-type and Nrf2-deficient mice were fed the following diets for 12 weeks: 1) control diet, 2) high-fat diet (HFD), 3) HFD plus hesperin (10 mg/kg, ip, daily), 4) HFD for 6 weeks followed by HFD supplemented with iron for 6 weeks (HFD/iron), and 5) HFD/iron plus hesperin; to investigate whether hesperin could improve hepatic steatosis and iron accumulation. RESULTS: HFD increased hepatic triglycerides in both genotypes and Hesperi; hesperin suppressed the increase in hepatic triglycerides in wild-type mice but did not reduce triglycerides in Nrf2-deficient mice; hesperin did not block hepatic iron accumulation in either genotype. [1] |
| Synonyms | 6-MSITC, 6MSITC, 6 MSITC |
| Molecular Weight | 205.34 |
| Formula | C8H15NOS2 |
| Cas No. | 4430-35-7 |
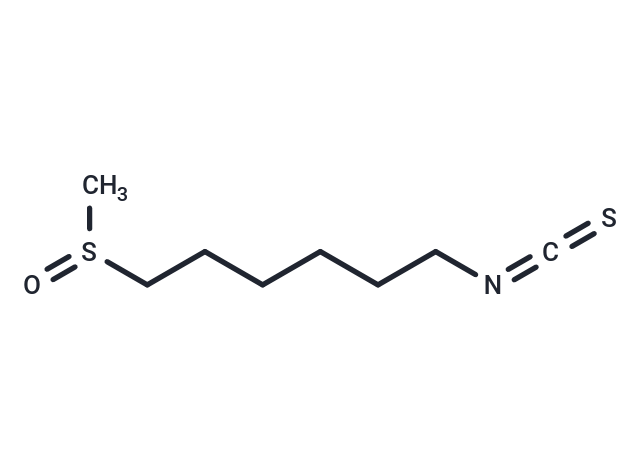
| Smiles | O=S(C)CCCCCCN=C=S |
| Relative Density. | 1.12 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 25 mg/mL (121.75 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.