Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Hemin (Hemin chloride) is a chlorinated iron-containing porphyrin, a heme oxygenase (HO)-1 inducer. Hemin has therapeutic activity in porphyrias by reducing heme deficiency in patients, thereby inhibiting δ-aminolevulinic acid synthetase activity through biochemical feedback.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $40 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $50 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Hemin (Hemin chloride) is a chlorinated iron-containing porphyrin, a heme oxygenase (HO)-1 inducer. Hemin has therapeutic activity in porphyrias by reducing heme deficiency in patients, thereby inhibiting δ-aminolevulinic acid synthetase activity through biochemical feedback. |
| Targets&IC50 | CYP3A4:2.4 μM, ANO1:0.45 μM, human caRD cellsiac voltage-gated sodium channel hNa V 1.5:80 nM, SARS-CoV-2:0.6805 μM (EC50), CYP1A2:27 μM, CYP2D6:19 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Pancreatic cancer cells PA-TU-8902, BxPC-3 and MiaPaCa-2 were treated with Hemin (30 µM) for 48 h. Cell viability was measured using the CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay. RESULTS: Hemin had a significant effect on cell proliferation of PA-TU-8902, BxPC-3 and MiaPaCa-2 cell lines, decreasing cell proliferation to 62±5%, 51±3% and 38±8%, respectively. [1] METHODS: Astrocyte cultures were treated with Hemin (25 µM) for 12-24 h. Iron content was measured using colorimetric method. RESULTS: Iron accumulation occurred in cultured astrocytes after incubation with Hemin. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To investigate the effects on renal injury, Hemin (100 µmol/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to BABL/c mice with renal ischemia-reperfusion. RESULTS: Hemin pretreatment promoted ERK1/2 phosphorylation and enhanced tubular recovery, thereby preventing further kidney injury. [3] METHODS: To investigate the effects on insulin resistance, Hemin (50 µmol/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to C57BL/6 mice on a high-fat diet once daily for four weeks. RESULTS: Hemin prevented the development of high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance by increasing insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle. [4] |
| Cell Research | In vitro effects of various statins and hemin, a heme oxygenase inducer, on cell proliferation were evaluated in PA-TU-8902, MiaPaCa-2 and BxPC-3 human pancreatic cancer cell lines. The effect of statins on heme oxygenase activity was assessed and heme oxygenase-silenced cells were used for pancreatic cancer cell proliferation studies. Cell death rate and reactive oxygen species production were measured in PA-TU-8902 cells, followed by evaluation of the effect of cerivastatin on GFP-K-Ras trafficking and expression of markers of invasiveness, osteopontin (SPP1) and SOX2[1]. |
| Synonyms | Hemin chloride |
| Molecular Weight | 651.94 |
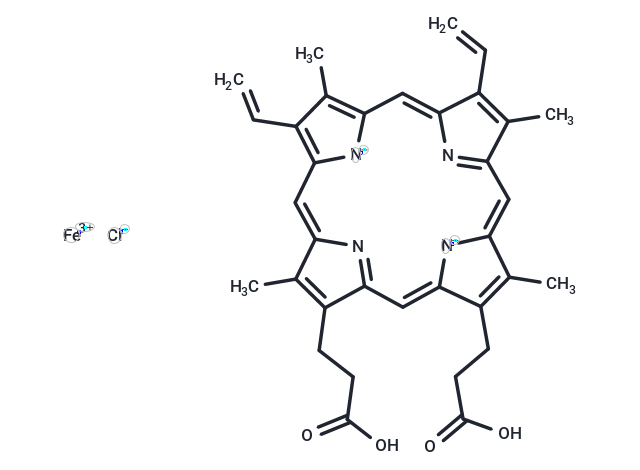
| Formula | C34H32ClFeN4O4 |
| Cas No. | 16009-13-5 |
| Smiles | [Cl-].[Fe+3].Cc1c(CCC(O)=O)c2cc3[n-]c(cc4nc(cc5[n-]c(cc1n2)c(C=C)c5C)c(C=C)c4C)c(C)c3CCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Color | Black |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 30 mg/mL (46.02 mM), Sonication is recommended. 0.1M NaOH: 25 mg/mL (38.35 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 0.05% DMSO+99.95% 0.1 M NaoH: 0.33 mg/mL (0.51 mM), Solution. 8% 0.1M NaOH+92% PBS: 2 mg/mL (3.07 mM), Solution, pH=7. 0.05%DMSO+99.95%PBS: 0.33 mg/mL (0.51 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.1M NaOH/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.