Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
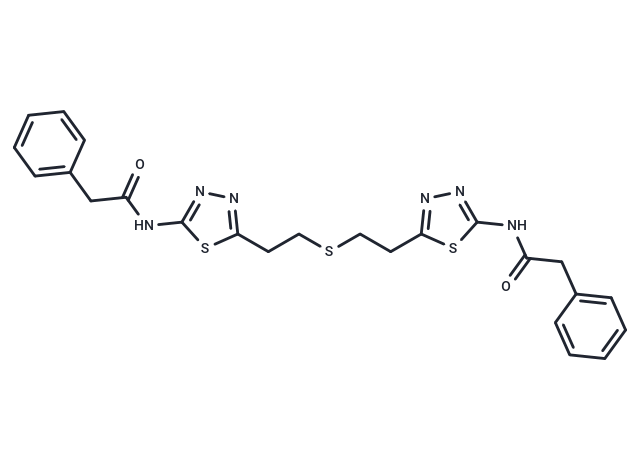
BPTES(IC50 of 0.16 μM) is an effective and specific GlutamiN/Ase GLS1 (KGA) inhibitor.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $31 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $44 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $63 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $81 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $153 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $229 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $342 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $497 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $813 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $81 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | BPTES(IC50 of 0.16 μM) is an effective and specific GlutamiN/Ase GLS1 (KGA) inhibitor. |
| Targets&IC50 | Glutaminase GLS1:0.16 μM |
| In vitro | BI-9564 with EC50 of 800 nM.BRD7 implied as a tumor suppressor and is down-regulated in cancer cells, BI-9564 shows Kd of 73 nM for it, and is >10-fold more selective for BRD9 over the high homologues bromodomain. BI-9564 (<5 μM) shows no activity against 324 kinases, when BI-9564 at 10 μM, an inhibition >40% is observed for only 2 out of 55 GPCRs. |
| In vivo | In LAP/MYC mice, BPTES (12.5 mg/kg, i.p.) prolongs survival with no significant effects on MYC, GLS, or GLS2 levels. BPTES (200 μg/mouse, i.p.) also inhibits tumor cell growth in mice harboring P493 tumor xenografts. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | Glutaminase Inhibition: Cell Free Assay: Assay plates are prepared containing 2 μL test compound in DMSO/well. The enzyme is diluted to 1 unit (liver) or 0.8 unit (kidney)/100 μL in glutaminase assay buffer, and 100 μL diluted enzyme is added to each well of the assay plate by Multidrop. The contents are mixed by shaking at full speed for 1 min on TiterMix 100. The plates are preincubated at room temperature (RT) for 20 min to allow binding of test compounds to glutaminase, and 50 μL glutamine solution (7 mM in assay buffer) is added to each well by Multidrop. The contents are shaken at full speed for 30 sec on TiterMix 100, and the plates are then incubated at RT for 60 min (liver) or 90 min (kidney). To stop the reactions, 20 μL HCl (0.3 N) is added to each well by Multidrop and mixed immediately by shaking for 30 sec on TiterMix 100. For quantification, glutamate (formed by glutaminase-catalyzed hydrolysis of glutamine) is oxidized to 2-oxoglutarate by a second enzyme, glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), with the concomitant production of the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Reduction of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) in the assay solution by NADH, catalyzed by phenazine methosulphate (PMS), results in the formation of a blue-purple formazan. The absorption of formazan at 540 nm is linearly proportional to the concentration of glutamate up to 200 μM. NBT/GDH reagent (50 μL) is added to each well by Multidrop and mixed by shaking for 30 sec on TiterMix 100, and the plates are incubated at RT for 20 min to allow color formation by the GDH reaction. Glutamate concentration is determined from formazan concentration as determined by reading OD540 nm on a SpectraMax 340. |
| Cell Research | BPTES is dissolved in DMSO. Cells are plated at a density of 500 cells/well in a 96-well black clear bottom plate. At 24 hrs, media is changed to the appropriate media (DMEM with 4.5 g/L, 1.5 g/L or 0.1 g/L glucose, 10% FBS, pencillin/streptomycin, and 4 mM glutamine with or without doxycyline). 48 hours after plating, compounds or DMSO are added. Media and alamarBlue is added to a volume of 200 μL in each well. Fluorescence is measured at 48 hrs or 72 hrs (EGCG) using a Victor3 plate-reader. |
| Molecular Weight | 524.68 |
| Formula | C24H24N6O2S3 |
| Cas No. | 314045-39-1 |
| Smiles | O=C(Cc1ccccc1)Nc1nnc(CCSCCc2nnc(NC(=O)Cc3ccccc3)s2)s1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.420 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 35.71 mg/mL (68.06 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.