 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

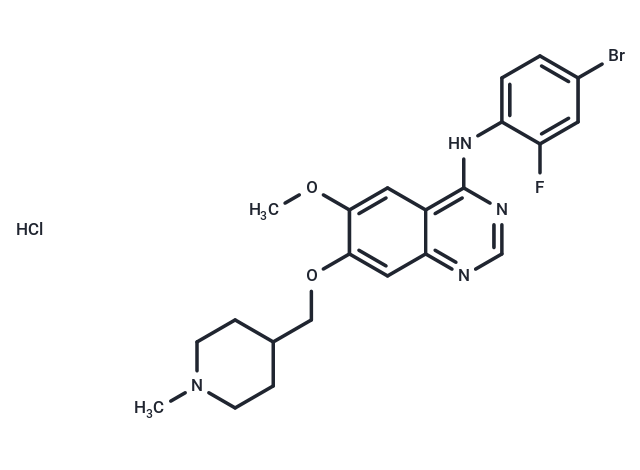
Vandetanib hydrochloride (D6474 hydrochloride) is a potent, orally active inhibitor of VEGFR2/KDR tyrosine kinase activity with an IC50 of 40 nM. It also exhibits activity against VEGFR3/FLT4 tyrosine kinase activity (IC50 = 110 nM) and EGFR/HER1 (IC50 = 500 nM) [1].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $1,520 | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks | |
| 50 mg | $1,980 | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks | |
| 100 mg | $2,500 | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks |
| Description | Vandetanib hydrochloride (D6474 hydrochloride) is a potent, orally active inhibitor of VEGFR2/KDR tyrosine kinase activity with an IC50 of 40 nM. It also exhibits activity against VEGFR3/FLT4 tyrosine kinase activity (IC50 = 110 nM) and EGFR/HER1 (IC50 = 500 nM) [1]. |
| Targets&IC50 | EGFR/HER1:500 nM, VEGFR3:110 nM, VEGFR2:40 nM |
| In vitro | Vandetanib effectively inhibits VEGFR3 and EGFR, showing IC50 values of 110 nM and 500 nM, respectively. It exhibits markedly less sensitivity towards PDGFRβ, Flt1, Tie-2, and FGFR1, with IC50 values ranging from 1.1 to 3.6 μM and demonstrates negligible activity against MEK, CDK2, c-Kit, erbB2, FAK, PDK1, Akt, and IGF-1R, all with IC50 values exceeding 10 μM. Notably, Vandetanib reduces the proliferation of HUVECs stimulated by VEGF, EGF, and bFGF, registering IC50 values of 60 nM, 170 nM, and 800 nM, respectively, while sparing unstimulated basal endothelial cell growth. Additionally, it varies in inhibiting tumor cell growth, with IC50 values ranging from 2.7 μM in A549 cells to 13.5 μM in Calu-6 cells. In contrast, Odanacatib demonstrates only weak inhibition of antigen presentation in a mouse B cell line (IC50 = 1.5±0.4 μM) and minimal effect on the processing of the MHC II invariant chain protein IiP10 in mouse splenocytes, when compared to the more potent Cat S inhibitor LHVS. Vandetanib also suppresses the phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 in HUVECs and EGFR in hepatoma cells, further inhibiting cell proliferation. |
| In vivo | Vandetanib (15 mg/kg, orally) demonstrates a markedly stronger anti-tumor effect compared to gefitinib in the H1650 xenograft model, with an IC50 value of 3.5±1.2 μM for tumor growth inhibition [3]. In mice with tumors, vandetanib administration at doses of 50 or 75 mg/kg leads to the suppression of VEGFR-2 and EGFR phosphorylation in tumor tissues. This results in a significant reduction of tumor vessel density, an increase in tumor cell apoptosis, inhibition of tumor growth, enhanced survival, decreased intrahepatic metastases, and elevated levels of VEGF, TGF-α, and EGF within the tumor tissues [4]. |
| Molecular Weight | 511.81 |
| Formula | C22H25BrClFN4O2 |
| Cas No. | 524722-52-9 |
| Smiles | Cl.COc1cc2c(Nc3ccc(Br)cc3F)ncnc2cc1OCC1CCN(C)CC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.31g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.