 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

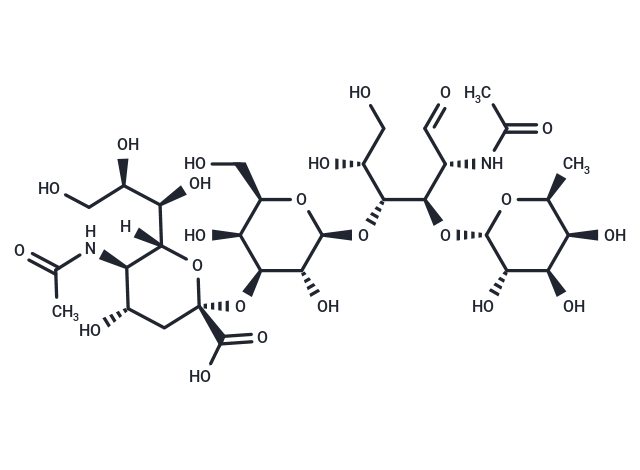
Sialyl-Lewis X (sLeX), a sialylated fucosylated tetrasaccharide and endogenous antigen, serves as a high-affinity ligand for selectins (E-, P-, and L-selectin)[1]. It interacts with ELAM-1 and CD62, consequently inhibiting CD62-mediated neutrophil recruitment to inflammation sites[2].
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $457 | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 5 mg | $1,360 | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | Sialyl-Lewis X (sLeX), a sialylated fucosylated tetrasaccharide and endogenous antigen, serves as a high-affinity ligand for selectins (E-, P-, and L-selectin)[1]. It interacts with ELAM-1 and CD62, consequently inhibiting CD62-mediated neutrophil recruitment to inflammation sites[2]. |
| In vitro | Sialyl-Lewis X (sLeX) serves as a high-affinity ligand for CD62. The use of antibodies, specifically mAb CSLEX (IgM; anti-sLeX), obstructs the CD62-mediated attachment of HL-60 cells to activated platelets. Moreover, liposomes integrated with glycolipids mimicking the sLeX configuration are effective in preventing the adhesion of HL-60 cells and human neutrophils. Notably, sLeX liposomes demonstrate a superior inhibitory capability on cell adhesion, exhibiting a tenfold greater affinity compared to Lex liposomes, achieving maximum inhibition at a lower concentration (1 µg/ml) compared to a partial (50%) inhibition achieved by Lex liposomes at a higher concentration (5 µg/ml). Additionally, a soluble human milk oligosaccharide containing the LeX structure also impedes the binding of neutrophils to activated platelets, wherein sLeX is identified as a substantially more effective inhibitor (30-fold) than its nonsialylated counterpart, Lex. Specifically, to attain a 50% reduction in neutrophil adhesion, sLeX requires only 2 µg/ml, in contrast to Lex, which necessitates 54 µg/ml. |
| Molecular Weight | 820.748 |
| Formula | C31H52N2O23 |
| Cas No. | 98603-84-0 |
| Smiles | [H][C@]1(O[C@@](C[C@H](O)[C@H]1NC(C)=O)(O[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H](O[C@H]([C@H](O)CO)[C@H](O[C@@H]2O[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@@H](NC(C)=O)C=O)[C@@H]1O)C(O)=O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.