 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Prexasertib dimesylate (LY2606368 dimesylate) is a highly selective, ATP-competitive, second-generation inhibitor of checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1), with a K_i of 0.9 nM and an IC_50 of <1 nM, and also effectively inhibits CHK2 (IC_50 = 8 nM) and RSK1 (IC_50 = 9 nM). Its mechanism induces double-stranded DNA breakage and replication catastrophe, leading to apoptosis, and demonstrates potent anti-tumor activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $52 | 5 days | 5 days |
| Description | Prexasertib dimesylate (LY2606368 dimesylate) is a highly selective, ATP-competitive, second-generation inhibitor of checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1), with a K_i of 0.9 nM and an IC_50 of <1 nM, and also effectively inhibits CHK2 (IC_50 = 8 nM) and RSK1 (IC_50 = 9 nM). Its mechanism induces double-stranded DNA breakage and replication catastrophe, leading to apoptosis, and demonstrates potent anti-tumor activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | Chk1:<1 nM (IC50), Chk1:0.9 nM (Ki), Chk2:8 nM (IC50) |
| In vitro | Prexasertib dimesylate (LY2606368 dimesylate) demonstrates significant inhibitory activity against various kinases, including MELK (IC 50 =38 nM), SIK (IC 50 =42 nM), BRSK2 (IC 50 =48 nM), and ARK5 (IC 50 =64 nM), by targeting mechanisms crucial for cell cycle progression and mitosis. It relies on CDC25A and CDK2 to induce DNA damage. Specifically, treatment with 33 and 100 nM concentrations for 7 hours causes DNA damage during the S-phase in HeLa cells, while pretreatment at concentrations ranging from 8-250 nM for 15 minutes inhibits CHK1 (S296) and CHK2 (S516) autophosphorylation in HT-29 cells. At a lower concentration of 4 nM over 24 hours, it induces a substantial cell cycle shift from G1 and G2-M to S-phase, accompanied by an increase in H2AX phosphorylation in U-2 OS cells. A concentration of 33 nM for 12 hours leads to chromosomal fragmentation in HeLa cells, and at 100 nM from 0.5 to 9 hours, it triggers replication stress and reduces the availability of RPA2 for DNA binding. Cell cycle analysis and Western blot analyses further confirm its impact, revealing DNA damage in the G2-M population and inhibition of CHK1 and CHK2 autophosphorylation at concentrations as low as 31 nM in HeLa and HT-29 cells respectively. |
| In vivo | Prexasertib dimesylate (LY2606368 dimesylate), administered subcutaneously (SC) at dosages of 1-10 mg/kg twice daily for three cycles (each comprising 3 days of treatment followed by 4 days of rest), demonstrated significant inhibition of tumor growth in xenograft models[1]. At a higher dosage of 15 mg/kg, administered SC, this compound effectively inhibited CHK1 in the blood and induced phosphorylation of H2AX (S139) and RPA2 (S4/S8), indicating rapid DNA damage[1]. These studies were conducted using female CD-1 nu-/nu- mice (26-28 g) implanted with Calu-6 cells. For the tumor growth inhibition study, dosages of 1, 3.3, or 10 mg/kg resulted in up to 72.3% reduction in tumor size. In pharmacokinetic analysis at 15 mg/kg, CHK1 levels in plasma were 7 ng/mL at 12 hours, decreasing to 3 ng/mL by 24 hours, with detectable phosphorylation of H2AX and RPA2 as early as 4 hours post-administration, demonstrating the compound's swift action in causing DNA damage. |
| Synonyms | LY2606368 dimesylate |
| Molecular Weight | 557.6 |
| Formula | C20H27N7O8S2 |
| Cas No. | 1234015-58-7 |
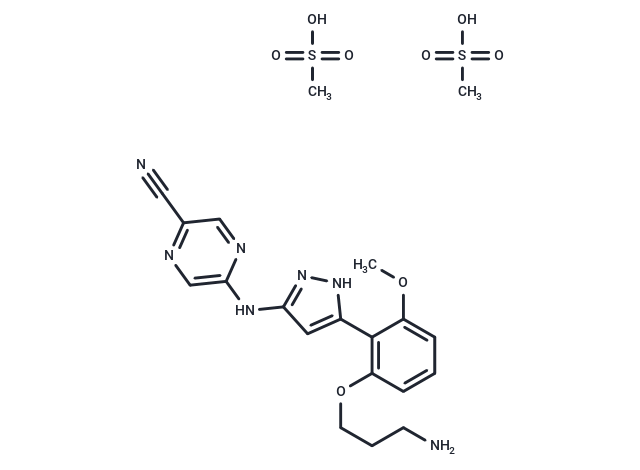
| Smiles | CS(O)(=O)=O.CS(O)(=O)=O.COc1cccc(OCCCN)c1-c1cc(Nc2cnc(cn2)C#N)n[nH]1 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.