 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

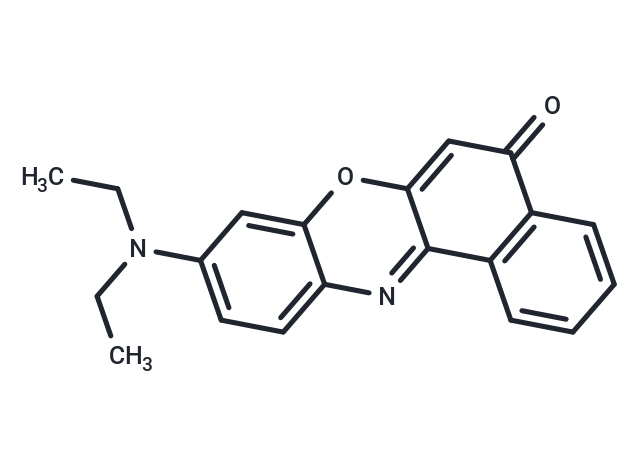
Nile Red (Nile Blue A oxazone) is a strongly fluorescent stain used for the detection of intracellular lipid droplets in the presence of a hydrophobic environment.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $41 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $53 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $64 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $101 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $147 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Nile Red (Nile Blue A oxazone) is a strongly fluorescent stain used for the detection of intracellular lipid droplets in the presence of a hydrophobic environment. |
| Cell Research | Instructions 1. Dissolve and preparation Nile Red can dissolve in DMSO, ethanol or acetone. The dissolution concentration is usually in the range of 0.2-10 μM, and the specific concentration should be optimized according to the needs of the experiment. 2. Cell staining 1. Staining procedure: 1) During cell culture, Nile Red can be used to label lipid droplets and neutral lipids in cells. The dissolved Nile Red solution can be added directly to the cell culture medium. 2) The commonly used staining concentration is 1-5 μM and the staining time is 10-30 minutes. During the staining process, cells are labeled with dyes, especially lipid droplets and fatty membranes. 3) After staining, you can use fluorescence microscopy or flow cytometry to observe. Nile Red produces a strong fluorescent signal on lipid droplets. 2. Fluorescence characteristics: Nile Red produces strong red fluorescence (Em ~ 620 nm) in lipid environments, while it manifests as golden fluorescence (Em ~ 540 nm) in low polarity environments. 2. Observation of lipid droplets and liposomes Nile Red can be used to study the formation and size of lipid droplets in cells. In flow cytometry, the number and size of lipid droplets can be quantitatively analyzed by observing the fluorescence intensity of Nile Red-labeled cells. Under a fluorescence microscope, the distribution and dynamic changes of lipid droplets can be observed with high resolution. 3. Fluorescence detection and quantification: Nile Red can also be used for quantitative analysis of lipids. By measuring its fluorescence intensity in the lipid solution, the amount of lipid in the sample can be inferred. Since the fluorescence intensity of Nile Red is related to the number and structure of lipids, it is a common tool for analyzing lipid content and evaluating fatty acid metabolism. 4. Co-staining experiment: Nile Red can be used in combination with other fluorescent dyes to label different types of lipids simultaneously, or to co-stain with other organelle markers, helping researchers to gain insight into the relationship between lipids and other cellular components. Notes: 1.Nile Red should be stored in a cool and dry environment to avoid strong light to prevent fluorescence attenuation. 2. The solution should be stored at -20°C to avoid repeated freeze-thawing. The above information is based on published literature. Experimental procedures should be appropriately modified to meet specific research demands. |
| Synonyms | Phenoxazone 9, Nile Blue A oxazone |
| Molecular Weight | 318.37 |
| Formula | C20H18N2O2 |
| Cas No. | 7385-67-3 |
| Smiles | CCN(CC)c1ccc2nc3c(cc(=O)c4ccccc34)oc2c1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.23g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 1.43 mg/mL (4.49 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.