 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

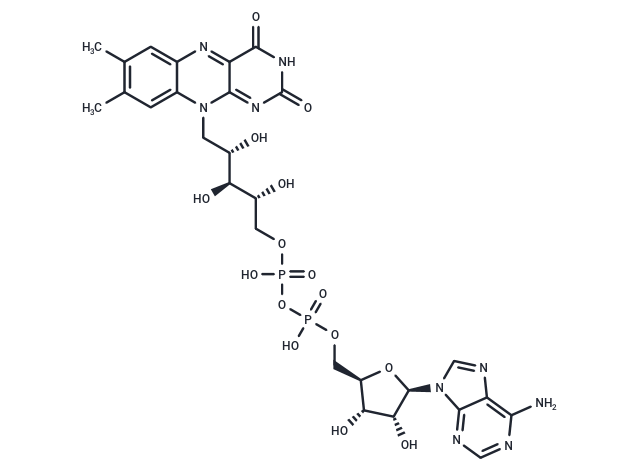
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a REDOX cofactor and protein cogroup involved in various metabolic reactions.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $37 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $53 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $88 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $129 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $192 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a REDOX cofactor and protein cogroup involved in various metabolic reactions. |
| In vitro | Characterized by an additional polymer-type redox reaction, Poly(Flavin adenine dinucleotide, FAD) is a highly effective electrocatalyst for NADH oxidation. Operating at the lowest potentials reported for NADH transducers (0.00 V, pH 7.4), poly(FAD) exhibits an electrochemical rate constant of 1.8 ± 0.6×10-3 cm/s, which is at the level of the NADH mass-transfer constant. Poly(FAD)-modified electrodes demonstrate dramatically improved stability and are the most advantageous NADH transducers for analytical chemistry[2]. |
| In vivo | Administered intravenously at a dose of 2 mg/kg, Flavin adenine dinucleotide significantly cancels the chlorpromazine (CPZ)-induced decrease in ventricular fibrillation threshold (VFT). The effect of CPZ on canine heart mitochondria is nullified by Flavin adenine dinucleotide. Following the injection of Flavin adenine dinucleotide, the dogs experience a transient hypotension within 10 minutes, after which their blood pressures recover to the initial level. Additionally, Flavin adenine dinucleotide prevents mitochondrial dysfunction induced by chlorpromazine[1]. |
| Synonyms | FAD |
| Molecular Weight | 785.55 |
| Formula | C27H33N9O15P2 |
| Cas No. | 146-14-5 |
| Smiles | C([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](COP(OP(OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N2C=3C(N=C2)=C(N)N=CN3)(=O)O)(=O)O)O)O)O)N4C=5C(=NC=6C4=CC(C)=C(C)C6)C(=O)NC(=O)N5 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,store at low temperature | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 125 mg/mL (159.12 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.