 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

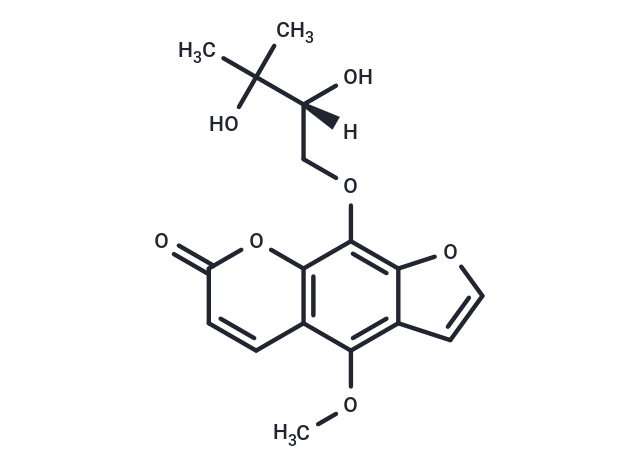
BYAKANGELICIN,a main furanocoumarin constituent isolated and characterized as an aldose reductase inhibitor,and is effective for the treatment of sugar cataracts and diabetic neuropathy and hence might be useful as a lead compound for the development of new type drugs for clinical use.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $31 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $73 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $123 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $198 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $297 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $453 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $88 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | BYAKANGELICIN,a main furanocoumarin constituent isolated and characterized as an aldose reductase inhibitor,and is effective for the treatment of sugar cataracts and diabetic neuropathy and hence might be useful as a lead compound for the development of new type drugs for clinical use. |
| In vitro | In human primary hepatocytes, byakangelicin markedly induced the expression of CYP3A4 both at the mRNA level (approximately fivefold) and the protein level (approximately threefold) but did not affect expression of human pregnane X receptor (hPXR).?Byakangelicin activated CYP3A4 promoter in a concentration-dependent manner (EC?? = 5 μM), and this activation was enhanced by co-transfection with hPXR.?The eNR4 binding element in the CYP3A4 promoter was required for the transcriptional activation of CYP3A4 by byakangelicin[1]. |
| In vivo | Cataract formation and galactitol accumulation in the lenses of rats fed a 30% galactose diet were significantly prevented by intragastric (i.g.) administration of byakangelicin at a dose of 100 mg/kg for 14 days. Administration of the drug for 18 days was found to suppress sorbitol accumulation and cause a significant reversal of depleted myo-inositol contents as well as Na(+),K(+)ATPase activity in the sciatic nerves of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. In rats, byakangelicin is effective for the treatment of sugar cataracts and diabetic neuropathy and hence might be useful as a lead compound for the development of new type drugs for clinical use[2]. |
| Cell Research | Cultures of human hepatocytes and a hepatoma cell line (Huh7 cells) were used.?mRNA and protein levels were measured by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and Western blot.?Plasmid constructs and mutants were prepared by cloning and site-directed mutagenesis.?Reporter (luciferase) activity was determined by transient co-transfection experiments[1]. |
| Animal Research | Induction of diabetes and drug treatment: Experimental diabetes was induced by a single injection of STZ (60 mg/kg), in 0.1 ml of 0.01 M citrate buffer (pH 4.5) into the tail vein of male Sprague-Dawley rats that had been fasted overnight.?Blood glucose was determined with a commercial blood glucose oxidase analysis kit.?Rats with blood glucose concentrations higher than 300 mg/dL were selected and considered to be diabetic.?Beginning with day 3 after the injection of STZ, diabetic rats were dosed with byakangelicin and epalrestat suspended in 5 g/dL gum arabic once a day throughout the experimental periods.?Controls and a group of normal rats were given the vehicle alone.?Animals were sacrificed by ether anesthesia and tissues were surgically removed, weighed and processed either for GC determination of polyol contents or for ATPase assay[2]. |
| Molecular Weight | 334.32 |
| Formula | C17H18O7 |
| Cas No. | 482-25-7 |
| Smiles | [H][C@@](O)(COc1c2occc2c(OC)c2ccc(=O)oc12)C(C)(C)O |
| Relative Density. | 1.373 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (134.6 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (5.98 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.