Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Sodium 4-aminosalicylate dihydrate (4-Amino-salicylic acid sodium salt) is the sodium salt form of aminosalicylic acid, an analog of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) with antitubercular activity. Sodium 4-aminosalicylate dihydrate exerts its bacteriostatic activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis by competing with PABA for enzymes involved in folate synthesis, thereby suppressing growth and reproduction of M. tuberculosis, eventually leading to cell death.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 g | $29 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Sodium 4-aminosalicylate dihydrate (4-Amino-salicylic acid sodium salt) is the sodium salt form of aminosalicylic acid, an analog of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) with antitubercular activity. Sodium 4-aminosalicylate dihydrate exerts its bacteriostatic activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis by competing with PABA for enzymes involved in folate synthesis, thereby suppressing growth and reproduction of M. tuberculosis, eventually leading to cell death. |
| In vitro | Following local perfusion with 7.5 mg/mL of 4-aminosalicylate, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid was detected in the intestines of anesthetized rats. |
| In vivo | 4-Aminosalicylate exhibits effective DPPH radical scavenging activity and rapidly neutralizes hydroperoxyl radicals in aqueous solutions, displaying a concentration-dependent cycle similar to that of Trolox or cysteine, indicative of chain-breaking antioxidant activity. At 0.65 mM, 4-aminosalicylate attenuates the lethal effects of superoxide radicals or hydrogen peroxide on Chinese hamster ovary cells. In cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages, aminosalicylate (25 mM) stimulates phospholipase D in a time- and concentration-dependent manner, and at 5 mM, it enhances protein kinase C activation of PLD. Post-treatment with 4-aminosalicylate (20 mM) results in a 260% increase in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate levels in macrophages. Furthermore, in isolated colonic mucosal cells, 4-aminosalicylate (0.1 mM) dose-dependently reduces the synthesis of LTB4, thereby decreasing the LTB4/PGE2 ratio. |
| Synonyms | Sodium 4-Aminosalicylate, 4-Amino-salicylic acid sodium salt |
| Molecular Weight | 211.15 |
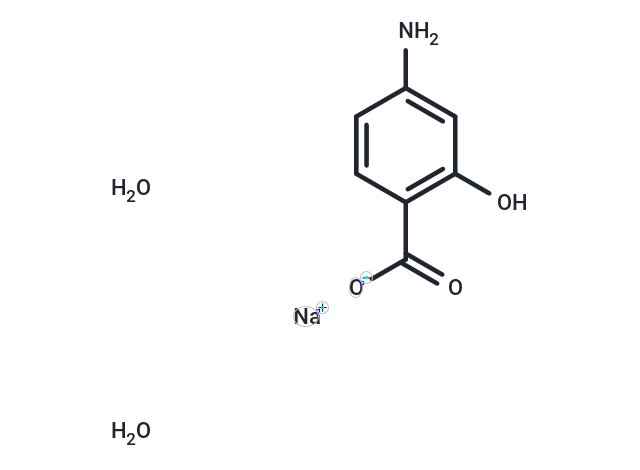
| Formula | C7H6NNaO3·2H2O |
| Cas No. | 6018-19-5 |
| Smiles | O.[Na+].Nc1cc(O)c(cc1)C(=O)[O-].O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 198.9 mM, Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 55 mg/mL (260.48 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (9.47 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.