Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
SB-657510 is a urotensin II (UII) receptor (UT) antagonist. The Ki values of UT for human, monkey, cat, rat and mouse were 61, 17, 30, 65 and 56 nM, respectively. SB-657510 plays an anti-inflammatory role by inhibiting UII-induced inflammatory mediators, such as adhesion molecules, in human vascular endothelial cells and upregulation of cytokines and tissue factors. SB 657510 has a therapeutic effect on diabetes-related atherosclerotic disease in diabetic mouse models.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $45 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $123 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $197 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $328 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $443 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $592 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $137 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | SB-657510 is a urotensin II (UII) receptor (UT) antagonist. The Ki values of UT for human, monkey, cat, rat and mouse were 61, 17, 30, 65 and 56 nM, respectively. SB-657510 plays an anti-inflammatory role by inhibiting UII-induced inflammatory mediators, such as adhesion molecules, in human vascular endothelial cells and upregulation of cytokines and tissue factors. SB 657510 has a therapeutic effect on diabetes-related atherosclerotic disease in diabetic mouse models. |
| Targets&IC50 | UTII receptor (rat):65 nM, UTII receptor (cat):30 nM, UTII receptor (mouse):56 nM, UTII receptor (human):61 nM, UTII receptor (monkey):17 nM |
| In vitro | The UII-induced increase in adhesion between U937 and EA.hy926 cells was blocked by SB-657510 dramatically. SB-657510 (1 μM; 0.5-8 hours) blocks the expression of tissue factor induced by UII in endothelial cells.[1] SB-706375 (1-10000 nM) inhibits [Ca2+]i mobilization elicited by 10 nM hU-II(IC50 of 180 nM).[2] |
| In vivo | The progression of high-fat diet-induced atherosclerosis and diabetes-associated atherosclerosis inhibited by SB-657510.[1] Levels of phosphorylated ERK are significantly attenuated in the aorta of SB-657510-treated (30 mg/kg/day) diabetic mice (Male Apoe KO mice).[3] |
| Molecular Weight | 505.81 |
| Formula | C19H22BrClN2O5S |
| Cas No. | 474960-44-6 |
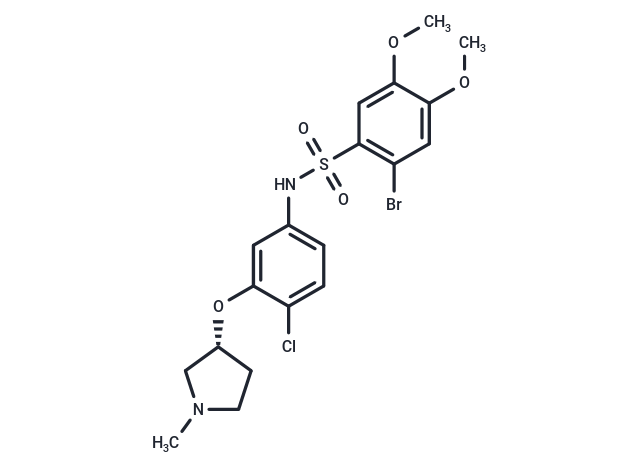
| Smiles | COc1cc(Br)c(cc1OC)S(=O)(=O)Nc1ccc(Cl)c(O[C@@H]2CCN(C)C2)c1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.512 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 27 mg/mL (53.38 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.