Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Protocatechuic acid (3, 4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid) (3, 4-dihydroxybenzoic acid) is a natural phenolic compound found in many edible and medicinal plants. Recent studies indicate that it could be used as a protective agent against cardiovascular diseases and neoplasms. The mechanism of its action is mostly associated with antioxidant activity, including inhibition of generation as well as scavenging of free radicals and up-regulating enzymes which participate in their neutralization.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $48 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $54 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Protocatechuic acid (3, 4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid) (3, 4-dihydroxybenzoic acid) is a natural phenolic compound found in many edible and medicinal plants. Recent studies indicate that it could be used as a protective agent against cardiovascular diseases and neoplasms. The mechanism of its action is mostly associated with antioxidant activity, including inhibition of generation as well as scavenging of free radicals and up-regulating enzymes which participate in their neutralization. |
| In vitro | Protocatechuic acid inhibits the aggregation of Aβ and αS and destabilizes their preformed fibrils that prevent the death of PC12 cells triggered by Aβ- and αS-induced toxicity[3]. |
| In vivo | Protocatechuic acid can prevent stress-induced immobility time in forced swim test without altering locomotor activity in mice. In addition, Protocatechuic acid treatment attenuates the elevation of serum corticosterone, lipid peroxidation and restores enzymatic antioxidants in cerebral cortex and hippocampus in ARS mice[1]. Rat administered cadmium and treated with prostigmine and doses of Protocatechuic acid (10−20 mg/kg) has significantly reduced BChE activity. Cadmium and either prostigmine or Protocatechuic acid (10−20 mg/kg) treated rats shows a marked reduction in MDA level[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | AChE activity investigation is carried out in a reaction mixture containing 50 μL of tissue homogenate, 50 μL of 5, 5'-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic) acid (DTNB), 1175 μL of 0.1 M phosphate-buffered solution, pH 8.0. After incubation for 20 min at 25°C, 25 μL of acetylthiocholine iodide solution is added as the substrate. The AChE activity is determined as changes in absorbance reading at 412 nm for 3 min at 25°C and using a UV/Visible spectrophotometer. |
| Cell Research | Protocatechuic acid is dissolved in DMSO. Dilutions of Protocatechuic acid (2, 5, 10, 20, 50, and 100 μM) are prepared from stock solutions, with serum-free culture medium. Equal volumes of each solution are mixed with Aβ1-42 (10 μM), then incubated for 24 h on a thermoblock, with continuous agitation, and then exposed to PC12 cells for 24 h to test whether Protocatechuic acid can prevent cell death triggered by Aβ. Cell viability is determined by MTT reduction assay. Cells are treated with 200 μL per well of MTT solution (final concentration, 0.5 mg/mL in DMEM-Glutamax medium) for 3 h, at 37°C, with 5% CO2. The dark blue formazan crystals that formed are solubilized with 100 μL per well of DMSO, for 30 min. Absorbance is measured at 540 nm, with a microplate reader. Results are expressed as the percentage of MTT reduction in relation to the absorbance of control cells at 100%. |
| Synonyms | Protocatechuate, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid, 3, 4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 154.12 |
| Formula | C7H6O4 |
| Cas No. | 99-50-3 |
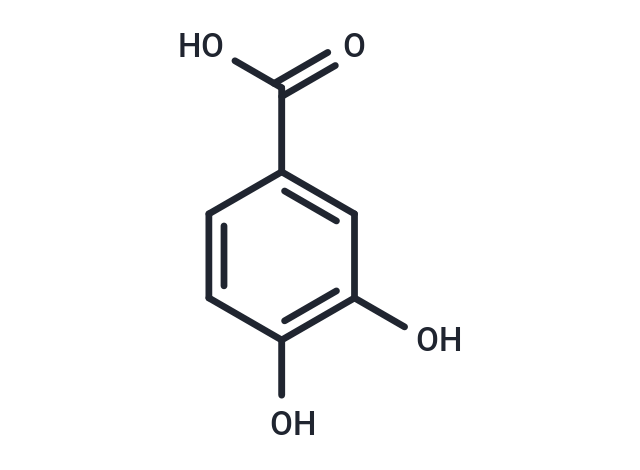
| Smiles | C(O)(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.54 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 5 mg/mL (32.44 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 96 mg/mL (622.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (12.98 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.