Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Lidamidine (Lidamidinum) is an effective antidiarrheal agent that inhibits intestinal secretion, reduces intestinal transit, and inhibits smooth muscle contraction.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $117 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $165 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $262 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $388 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $592 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $828 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,110 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $1,480 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Lidamidine (Lidamidinum) is an effective antidiarrheal agent that inhibits intestinal secretion, reduces intestinal transit, and inhibits smooth muscle contraction. |
| In vivo | Fasted male rats were anesthetised and equipped with an intraluminal cannula positioned at the proximal end of a 10 cm fluid-filled segment of the ascending colon (basal pressure, 10 cm H2O). Intraluminal pressure was monitored by a transducer attached to a closed fluid-filled system. All drugs were administered intravenously by slow infusion. A regular pattern of distinct contractile complexes was observed over a 70 min period. These contractions increased intraluminal pressure to 39 +/- 1.2 cm H2O (mean +/- S.E.), occurred at a frequency of 0.3 per min and lasted from 1 to 2.5 min. Inhibition of these contractile patterns was observed with either atropine (0.1 mg/kg) or lidamidine (3.0 mg/kg). A 20 min pretreatment with idazoxan (3.0 mg/kg) antagonized lidamidine's but not atropine's effect. Trimazosin (1 mg/kg) or propranolol (0.3 mg/kg) pretreatment did not antagonize the lidamidine-generated inhibition[1]. |
| Synonyms | Lidamidinum, Lidamidina |
| Molecular Weight | 220.27 |
| Formula | C11H16N4O |
| Cas No. | 66871-56-5 |
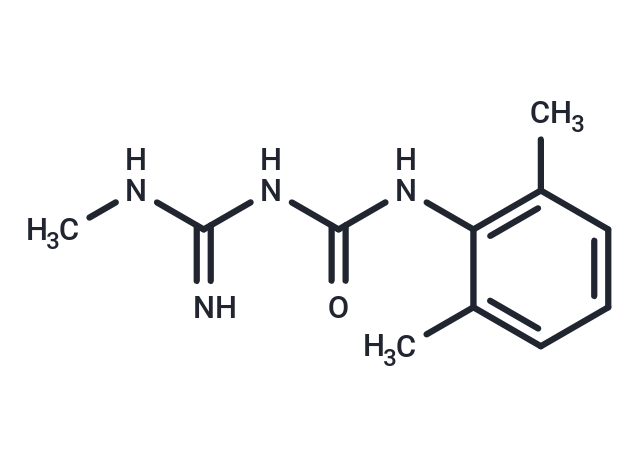
| Smiles | CNC(=N)NC(=O)NC1=C(C)C=CC=C1C |
| Relative Density. | 1.17g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 5 mg/mL (22.7 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.