Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
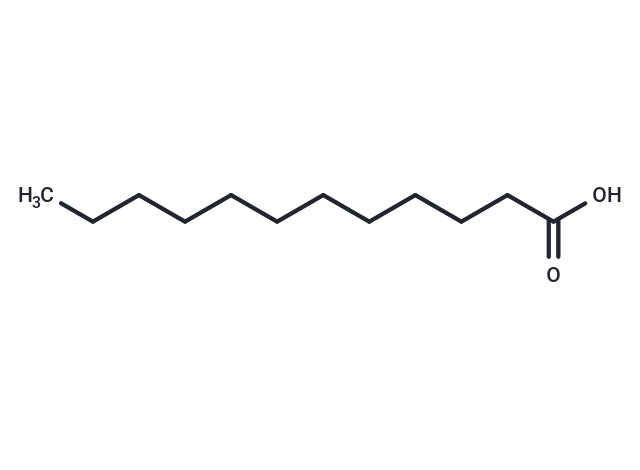
Lauric Acid (Dodecylic acid),which is found naturally in various plant and animal fats and oils, is a saturated medium-chain fatty acid with a 12-carbon backbone. It is a major component of coconut oil and palm kernel oil.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 g | $33 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Lauric Acid (Dodecylic acid),which is found naturally in various plant and animal fats and oils, is a saturated medium-chain fatty acid with a 12-carbon backbone. It is a major component of coconut oil and palm kernel oil. |
| Targets&IC50 | S. epidermidis:4 μg/mL(EC50), S. aureus:6μg/mL(EC50), P. acnes:2μg/mL(EC50) |
| In vitro | Lauric acid induces apoptosis in Caco-2 (p<0.05) and IEC-6 cells (p<0.05). In Caco-2 cells, lauric acid reduces GSH availability and generated ROS compared to butyrate(p < 0.05). Lauric acid reduces Caco-2 and IEC-6 cells in G0/G1 and arrested cells in the S and G2/M phases. Lauric acid induces apoptosis in IEC-6 cells compared to butyrate(p < 0.05). Lauric acid induces high levels of ROS[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | JAK2 and other human kinase activity assays: JAK2 kinase activity was assessed with the HTScan JAK2 Kinase Assay Kit per manufacturer's protocol. The possible effects of FLLL32 on the other 10 purified human protein kinases were determined by using a Kinase Profiler Assay. |
| Cell Research | Cell lines are harvested by enzymatic dissociation and seeded into 24-well tissue culture plates at 2.5 × 105 and 1.5 × 105 cells/ml, respectively. After 24 h of incubation, the medium is replaced with 1 ml of complete DMEM containing freshly prepared (50 mM )Lauric acid, conjugated to 0.4% FAF-BSA to final concentrations of 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 and 1 mM and compared to NaB (5 mM ) with 50 μl of 0.4% FAF-BSA as a vehicle control and incubated in a humidified atmosphere at 37℃ in 5% CO2 and, after enzymatic dissociation, assayed at 24, 48, 72, and 96 h. All experimental studies are undertaken in triplicate and measured in duplicate. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | N-Dodecanoic acid, Dodecylic acid, dodecanoic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 200.32 |
| Formula | C12H24O2 |
| Cas No. | 143-07-7 |
| Smiles | CCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 0.883 g/cm3 at 25℃ (lit.) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 38 mg/mL (189.7 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 260 mg/mL (1297.92 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 16 mg/mL (79.87 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/Ethanol/DMSO
Ethanol/DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.