Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Icariside E4 is a natural compound derived from Ulmus minor that acts via AMPK phosphorylation and inhibition of MID1IP2 hypolipidation in HepG1 cells.Icariside E4 has anti-injurious, antioxidant, anti-Alzheimer's and anti-inflammatory effects and inhibits SREBP-1c, liver X receptor-α (LXR) and FASN in Icariside E4 is an effective candidate for the treatment of fatty liver disease and has hypolipidemic potential in HepG1 cells.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $1,620 | Backorder | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $1,980 | Backorder |
| Description | Icariside E4 is a natural compound derived from Ulmus minor that acts via AMPK phosphorylation and inhibition of MID1IP2 hypolipidation in HepG1 cells.Icariside E4 has anti-injurious, antioxidant, anti-Alzheimer's and anti-inflammatory effects and inhibits SREBP-1c, liver X receptor-α (LXR) and FASN in Icariside E4 is an effective candidate for the treatment of fatty liver disease and has hypolipidemic potential in HepG1 cells. |
| Targets&IC50 | DPPH:5.6 μg/mL |
| In vitro | IE4 did not show any toxicity in HepG2 cells, but reduced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells by Oil Red O staining. IE4 activated phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC and inhibited the expression of MID1IP1 in HepG2 cells. Furthermore, IE4 suppressed the expression of SREBP-1c, liver X receptor-α (LXR), and FASN for de novo lipogenesis in HepG2 cells. IE4 has hypolipogenic potential in HepG2 cells via activation of AMPK and inhibition of MID1IP1 as a potent candidate for the treatment of fatty liver disease.[2] |
| Molecular Weight | 506.54 |
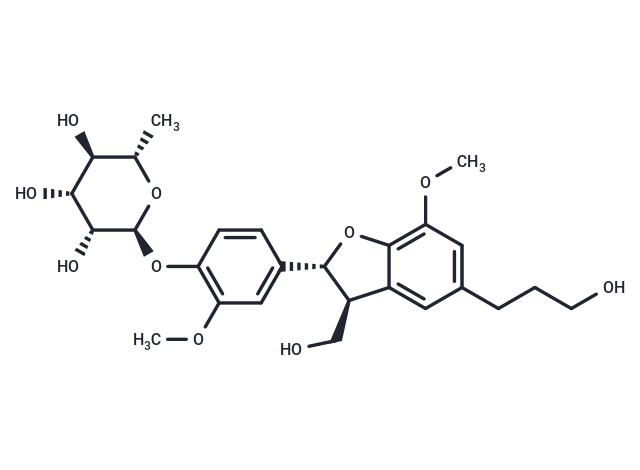
| Formula | C26H34O10 |
| Cas No. | 126253-42-7 |
| Smiles | C(O)[C@@H]1C=2C(O[C@H]1C3=CC(OC)=C(O[C@H]4[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)O4)C=C3)=C(OC)C=C(CCCO)C2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.348 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | store at low temperature,keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.